Finding undervalued companies in today’s stock market is still possible if you know the ideal criteria, ratios, and tools to use.
To find undervalued stocks, use established financial ratios such as discounted cash flow, the margin of safety, PEG, price to book, or the price to Graham number.
Each ratio provides a unique insight into a company to determine if it is undervalued.
This article will guide you through each ratio and the value investing criteria to help you select the right method to find high-quality, undervalued stocks.
What is an Undervalued Stock?
Undervalued stocks are trading at a significant discount to the value the stock market places on the share price. If a stock price is $10 and a company’s book value is $20 per share, one could estimate the stock is undervalued by 50%.
Using ratios and calculations, such as discounted cash flow, future earnings, the margin of safety, and fair value, you can find undervalued stocks selling at a discount.
Finding Undervalued Companies
To find undervalued companies, you need to estimate their worth. Warren Buffett values a company based on the future cash flow it can generate. Benjamin Graham developed the price-to-Graham number to value a company. Bruce Greenwald developed Earnings Power Value to value a company.
13 Great Ways To Find Undervalued Stocks
1. Select the right tools
To effectively and efficiently find undervalued stocks, you will need to use a stock screener to sort, filter, and research potential value stocks. Many free stock screeners are available online, but only a few are tailored specifically to find value stocks.
| Value Stock Screeners | Stock Rover | Portfolio123 | TradingView | Finviz |
| ⚡ Financial Metrics | 650 | 240 | 48 | 31 |
| 🏆 Intrinsic Value | ✓ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| 🎯 Margin of Safety | ✓ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| ♲ Graham Number | ✓ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| 📈 PEG Ratio | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 📊 PE Ratio | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 📕 Price to Book | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 🔍 Backtesting | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 🆓 Free | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| 🎮 Free Trial | 14-Day | 21 Days $9 | 30-Day | 30-Day |
| ✂ Discount | -25% | No | -50% | -37% |
| 🌎 Region | USA | USA | Global | USA |
Stock Rover is the best screener for value investors because it has the complete complement of value investing calculations built-in, including intrinsic value, fair value, the margin of safety, the Graham number, and the Greenblatt and Lynch ratios.
2. Use Intrinsic Value/Fair Value
A professional way to find undervalued stocks is to calculate the intrinsic value/fair value. The Intrinsic Value of a stock is an estimate of a stock’s value without regard for the stock market’s valuation. Two popular models are the Dividend Discount Model (DDM) and the Discounted Forward Cashflow (DFC) Model. There are multiple variations of intrinsic value; see our detailed article on intrinsic value.

Buffett bases his intrinsic value/fair value calculations on future free cash flows. Buffett thinks cash is a company’s most important asset, so he projects how much future cash a business will generate and discounts it against inflation. This is called the Discounted Cashflow Method.
⚡ Undervalued Stock Criteria: Intrinsic Value per Share > Stock Price
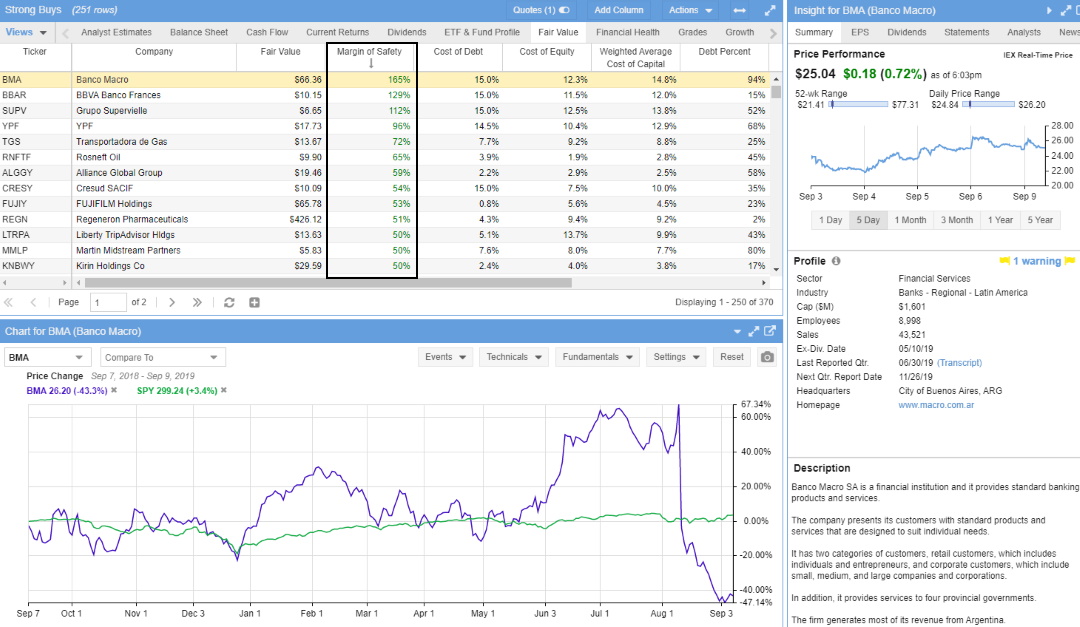
3. Use The Margin of Safety
Finding undervalued stocks using the Margin of Safety is a perfect addition to the intrinsic value calculation. The Magin of Safety is the difference between intrinsic value per share and the actual stock price.
If a stock price is significantly below a company’s actual Fair Value, that percentage difference is known as the Margin of Safety. Essentially, it is the percentage by which the stock market undervalues a company.
Buffett’s most important measure in deciding whether to invest in a company, the Margin of Safety, is the percentage difference between its Fair Value/Intrinsic Value and its actual stock price. This metric is the most important company valuation metric, as it is the final output of a detailed discounted cash flow analysis.
⚡ Undervalued Stock Criteria: Margin of Safety > 30%
4. The PEG Ratio
A simple way to find undervalued stocks is using the Price Earnings to Growth Forward Ratio, or PEG. PEG attempts to improve Price/Earnings comparisons by accounting for earnings growth.
PEG is calculated by dividing the forward Price/Earnings Ratio for the next 12 months by the estimated Earnings Per Share (EPS) growth for the next five years. The lower the PEG value, the more undervalued a stock is. A PEG value of 1 suggests perfect pricing.
⚡ Undervalued Stock Criteria: Price Earnings Growth < 1
5. The Price to Graham Number
You can find undervalued stocks using the Price to Graham Number. Created by the king of value investing, it is a conservative valuation measure highlighted in his seminal book The Intelligent Investor.
The Graham Number is one of his tests for whether a company is undervalued and is computed as the square root of 22.5 times the tangible book value per share times the diluted continuing earnings per share. A price to Graham Number less than 1 suggests a company is undervalued.
⚡ Undervalued Stock Criteria: Price to Graham Number < 1.0
6. Price to Lynch Fair Value
A great way to identify undervalued stocks is using the Price to Lynch Fair Value ratio. Price to Lynch is based on the legendary investor Peter Lynch’s valuation formula featured in his book One Up on Wall Street.
The price-to-Lynch fair Value ratio divides the stock price by the PEG rate times the 5-year EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization) growth rate multiplied by continuing earnings per share. A price-to-Lynch fair value of less than 1.0 means the stock is undervalued.
⚡ Undervalued Stock Criteria: Price to Lynch Fair Value < 1.0
7. Greenblatt Earnings Yield
Joel Greenblatt’s Earnings Yield calculation allows you to find value stocks by comparing a company’s operating income to its enterprise value. Using the Greeblatt Earning Yield and the Greenblatt Return on Capital calculations is the core of his value investing methodology, which is featured in his “The Little Book that Beats the Market.”
This variation of earnings yield compares Operating Income (Earnings Before Interest & Taxes) to Enterprise Value.
⚡ Undervalued Stock Criteria: Greenblatt Earnings Yield > 3%
8. Price to Book Value
Using Price to Book Value identifies undervalued companies, but it does have issues due to what a company includes in Book Value in its accounting practices. Price to book value compares a stock’s market value to the value of total assets minus total liabilities.
Book Value is an appraisal of all a company’s assets. A good definition of book value is anything the company can sell for cash now. Book value assets include real estate, equipment, inventory, accounts receivable, raw materials, investments, cash assets, intellectual property rights, patents, etc. (book value). Also known as P/B or PB, a low P/B ratio could mean the stock is undervalued. However, it could also mean something is fundamentally wrong with the company.
⚡ Undervalued Stock Criteria: Price to Book Value – Lower is better
9. Price to Tangible Book Value
Price-to-tangible book Value is a better way of finding undervalued stocks than the price-to-book calculation. Price-to-tangible book value compares a stock’s market value to the value of total assets, less total liabilities and intangibles.
Removing the intangible assets from the calculation is a way to eliminate companies that may inflate the value of assets such as patents, trademarks, or brands. A low Price to Tangible ratio could mean that the stock is undervalued.
⚡ Undervalued Stock Criteria: Price to Tangible Book Value – Lower is better
10. PE Ratio
Although many websites recommend it, the Price-Earnings Ratio (PE ratio) is a flawed way to identify undervalued companies. It is only useful when comparing competitors in the same industry with similar business models.
The Price-Earnings Ratio (PE Ratio or PER) is a formula for performing a company valuation. It is calculated by dividing the current stock price by the previous 12 months earnings per share (EPS). A PE Ratio of 12 means you would pay $12 for every $1 of earnings if you invested.
⚡ Undervalued Stock Criteria: PE Ratio < 4th decile in the industry segment
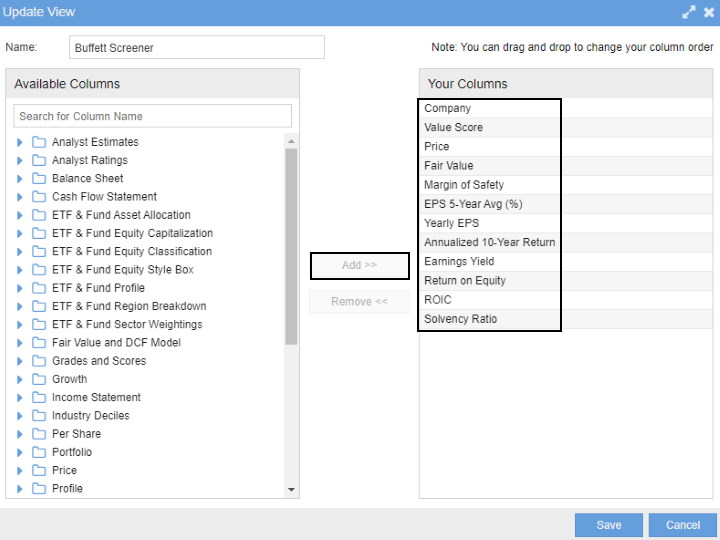
11. Finding undervalued stocks with Stock Rover
The most powerful way to find undervalued stocks is to use Stock Rover, which has the best selection of value investing metrics in the industry. Follow these steps to find the best-undervalued stocks.
- Register for a Free Premium Trial with Stock Rover
- Import the “Buffettology Inspired” Screener or create a new screener with the following criteria:
- Margin of Safety* > 20%
- Fair Value > Than Share Price
- Yearly EPS growth YOY > 5%
- Return on Equity (ROE) 0 > 15%
- 10-Year ROIC Average* => 12%
Full details on this screening technique are here: Value Investing Strategy: 7 Proven Value Stock Screeners.
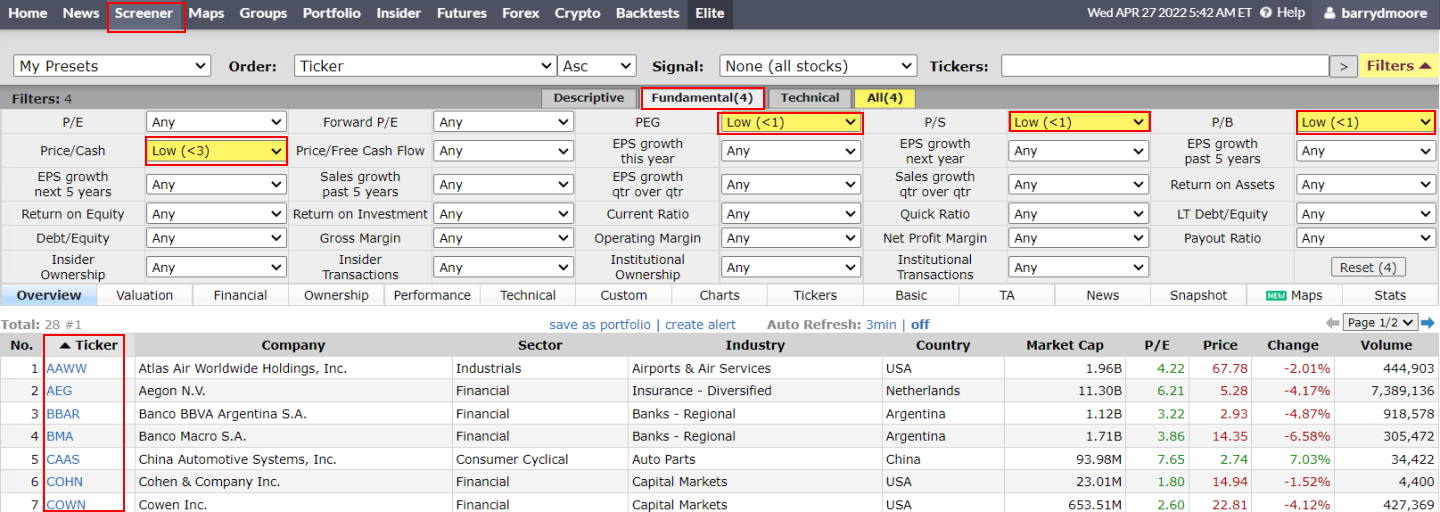
11. Using Finviz for Undervalued Stocks
Finviz is a powerful stock screening tool that helps you find undervalued stocks. With Finviz, you can create a custom screener with the following criteria:
- Visit Finviz
- Select the screener tab
- Select the fundamental tab
- Implement the following criteria
- Price/Cash – Low <3
- PEG – Low <1
- P/S – Low <1
- P/B – Low <1
12. Find Undervalued for Free with TradingView
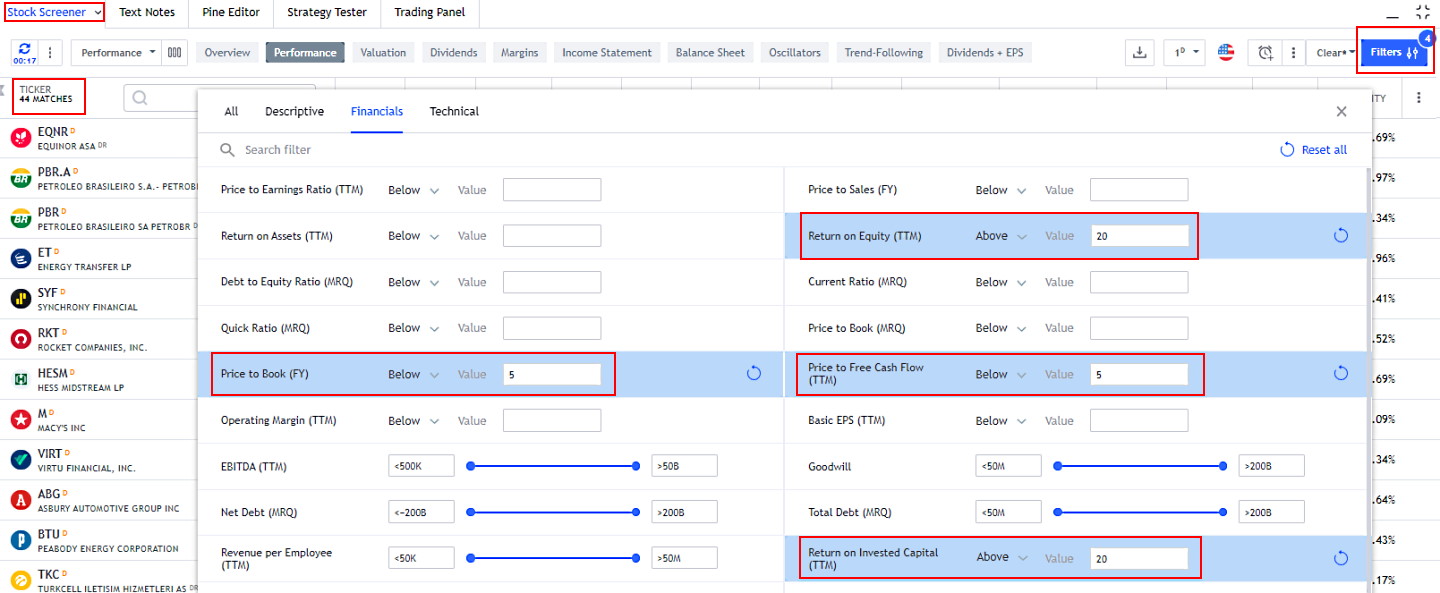
You can find undervalued stock using TradingView for free. The key criteria are Return on Equity, Price to Book, Price to Free Cash Flow, and Return on Invested Capital.
- Visit TradingView
- Select Stock Screener
- Select Financials and enter the following criteria
- Price to Book <5
- Return on Equity >20
- Price to Free Cashflow <5
- Return on Invested Capital >20
13. Look for stocks with hidden value
Benjamin Graham advised investors to look for stocks in companies with values the market could not see—for example, a retailer with a low stock price but extensive real estate holdings. The retailer’s business might lose money, but the property its stores sit on could be valuable.
Another example of a low-priced value stock is a company that produces a commodity vital to a growing industry. For instance, in a lithium mining company, lithium is the main ingredient in the batteries laptops, smartphones, and electric cars rely on.
Why are stocks undervalued?
Stocks are undervalued because the market is often a poor judge of value. In particular, market players cannot see or appreciate many of the attributes that enable companies to make money. For example, few investors understood the potential value of e-commerce like Jeff Bezos did.
Also, institutional investors and speculators who drive the market often have a poor understanding of what they are selling. For instance, many investors know little about the stocks they own, trade, or speculate on.
Finally, most investors and speculators are short-term thinkers. Hence, they fail to grasp the long-term potential of companies like Amazon.
[Related Article: How To Find Value Stocks & Invest Like Warren Buffett]
Why is the stock market bad at stock valuation?
One explanation of why stocks can be undervalued is what investor, philosopher, and former trader Nassim Nicholas Taleb calls the “Green Lumber Fallacy.”
To explain, in his book, Antifragile Taleb claims he once knew a commodities trader who made a fortune trading green lumber futures. However, Taleb claims the trader did not realize green lumber is wood or know what they use it for.
Taleb thinks the trader made money because he was lucky enough to invest in the right commodity at the right time. Consequently, the Green Lumber Fallacy is the erroneous belief that traders, speculators, or investors are experts in what they are trading, speculating, or investing in.
Many stocks are undervalued because the participants in the market do not understand them. However, many people believe market participants understand what they are trading. Thus, most people believe the Green Lumber Fallacy and think the market is an accurate pricing mechanism.
You want to be a successful stock investor but don’t know where to start.
Learning stock market investing on your own can be overwhelming. There’s so much information out there, and it’s hard to know what’s true and what’s not.
Liberated Stock Trader Pro Investing Course
Our pro investing classes are the perfect way to learn stock investing. You will learn everything you need to know about financial analysis, charts, stock screening, and portfolio building so you can start building wealth today.
★ 16 Hours of Video Lessons + eBook ★
★ Complete Financial Analysis Lessons ★
★ 6 Proven Investing Strategies ★
★ Professional Grade Stock Chart Analysis Classes ★
Are undervalued stocks good?
Yes, numerous academic studies testing value stock selection have proven that a value stock strategy can lead to higher returns than investing in the market as a whole.
Undervalued stocks offer investors an opportunity to buy stock at prices below what they are worth. They are typically out of favor and may be overlooked by investors who focus on short-term performance rather than looking at the company’s fundamentals. As such, these stocks often represent good value investments. Investors who are able to identify undervalued stocks can potentially benefit from price appreciation once the market re-evaluates the company and its stock price, which could result in higher returns than investing in a passive index fund that tracks the broader market.
Investing in undervalued stocks also allows investors to manage risk since they are buying shares at a discount.
Can undervalued stocks be a bad idea?
Even though undervalued stocks represent a potential opportunity for investors, there are risks associated with investing in these stocks. Suppose the company is truly undervalued due to a fundamental problem, such as weak financials or poor management. In that case, the stock may not recover and could result in losses for an investor.
Ever Dreamed of Beating the Stock Market
Most people think that they can't beat the market, and stock picking is a game only Wall Street insiders can win. This simply isn't true. With the right strategy, anyone can beat the market.
The LST Beat the Market Growth Stock Strategy is a proven system that has outperformed the S&P500 in 8 of the last 9 years. We provide all of the research and data needed to make informed decisions, so you no longer have to spend hours trying to find good stocks yourself.
The LST Beat the Market System Selects 35 Growth Stocks and Averages a 25.6% Annual Return
★ 35 Stocks That Already Beat The Market ★
★ Buy The Stocks & Hold For 12 Months - Then Rotate ★
★ Fully Documented Performance Track Record ★
★ Full Strategy Videos & eBook ★
Take The Pain Out Of Stock Selection With a Proven Strategy
FAQ
What is the best software for undervalued stocks?
Stock Rover is the best software for finding and researching undervalued stocks. According to our testing, it has the complete set of all value investing criteria, ratios, and financials. Finviz and Portfolio 123 are also worth trying.
What are undervalued stocks?
Undervalued stocks are shares that trade for less than their intrinsic value, for example, the value of assets and future cash flow. They might be priced low due to market volatility, economic factors, or investor sentiment.
How do I identify undervalued stocks?
To identify undervalued stocks, use a stock screener to filter and analyze financial ratios like intrinsic value, margin of safety, PEG ratio, and the price to Graham number. Additionally, a low P/E ratio compared to industry peers with similar profit margins could indicate an undervalued stock.
What is the benefit of investing in undervalued stocks?
Investing in undervalued stocks offers the potential for high returns when the market corrects the price. It's a form of value investing that seeks to profit from market inefficiencies.
Are undervalued stocks risky?
Undervalued stocks can offer great returns and theoretically lower risk, but risks remain. The stock may be undervalued due to undisclosed business or financial problems. Always conduct thorough research before investing.
How do I calculate the intrinsic value of a stock?
Calculating the intrinsic value involves estimating future cash flows and discounting them to present value. This can be done using discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis.
Do undervalued stocks pay dividends?
Yes, many undervalued stocks pay dividends. These stocks can attract income-focused investors looking for capital appreciation and income generation. Value investors actively seek out undervalued stocks that pay dividends.
How long should I hold undervalued stocks?
The holding period for undervalued stocks is usually long-term because it might take time for the market to realize the company's intrinsic value. Some investors hold until the stock reaches its estimated intrinsic value, while others may hold longer.
Can a growth stock be undervalued?
Yes, a growth stock can be undervalued if its price doesn't reflect its future earnings potential. Valuing growth stocks can be difficult, so the market may not always price them correctly. Investors who can identify undervalued growth stocks stand to benefit from the potential for capital appreciation in addition to dividend payments.
What is the difference between undervalued and overvalued stocks?
An undervalued stock trades for less than its intrinsic value, offering profit potential. An overvalued stock, on the other hand, trades above its intrinsic value, indicating it may be overpriced and introducing higher risk into the investment.
Can blue-chip stocks be undervalued?
Yes, even blue-chip stocks can become undervalued. Market conditions, economic factors, or company-specific issues can lead to these established companies being undervalued.
Is investing in undervalued stocks a form of value investing?
Yes, investing in undervalued stocks is a key principle of value investing. Value investors seek stocks they believe are undervalued by the market, aiming to profit when the price corrects.
What's the difference between undervalued and penny stocks?
Penny stocks typically have a low price but are higher-risk investments because the company may have little value. Undervalued stocks may have higher prices, but they offer the potential of a greater return on investment because the value of their assets and future cashflows is worth more than the stock price.

