Swing trading is a popular investment strategy that capitalizes on short-term price movements.
Unlike day trading, which focuses on quick trades within a day, swing trading is more profitable, capturing larger price movements over days to weeks.
Swing trading originated in the early 20th century when traders started taking advantage of short-term price fluctuations. Over time, it has evolved to incorporate technical analysis and advanced trading tools.
Today, swing trading is widely practiced by both professional traders and individual investors.
What is Swing Trading?
Swing trading involves buying and selling financial instruments, such as stocks, currencies, or commodities, to profit from short-term price swings. Traders seek to identify patterns and trends that can predict future price movements.
Key Swing Trading Concepts:
- Price Swings are fluctuations in price that occur over a defined period. The timeframe is the duration for which a swing trade is held, typically ranging from a few days to a few weeks.
- Technical Analysis: Using historical price data, indicators, and chart patterns to make trading decisions.
- Fundamental Analysis involves examining a company’s financial reports, news releases, and other public data to assess its prospects.
- Risk Management: Strategies for mitigating risk and controlling losses by establishing entry and exit points, setting stop-loss orders, etc.
- Using Real-time News: Keeping up to date on the latest financial news and events and watching for breaking news that could impact price movements.
- Position Sizing: Calculating the optimal size of a trade based on the trader’s risk tolerance and account size.
- Developing Custom Indicators: Develop indicators and other technical tools to automate trading decisions or improve accuracy.
Pros
Swing trading offers several advantages for beginner investors, including higher returns, less effort, and better pattern and indicator success probabilities.
- Our chart indicator tests show that win percentages over days to weeks are far superior to day trading.
- Potential for Higher Returns: By capitalizing on short-term price movements, swing traders can achieve higher returns than long-term investing.
- Accessible for Part-Time Traders: Swing trading does not require constant monitoring of the markets, making it suitable for individuals with limited time.
- Diversification: Swing trading allows investors to diversify their portfolios by exploring different markets and sectors.
Cons
The cons of swing trading are higher risks, pricing pressure, and costs/slippage.
- Higher Risk: The potential for higher returns comes with a greater risk of losses.
- Pricing Pressure: Market makers can make it difficult to successfully swing trade in highly liquid stocks due to the pricing pressure they can exert on stock prices.
- Costs: Swing trading may incur additional costs such as commissions and other fees associated with trading.
Swing Trading Examples
To understand swing trading, we will explore two real academically proven examples of trading: the 82% reliable Cup and Handle pattern and the 89% percent Inverse Head and Shoulders pattern.
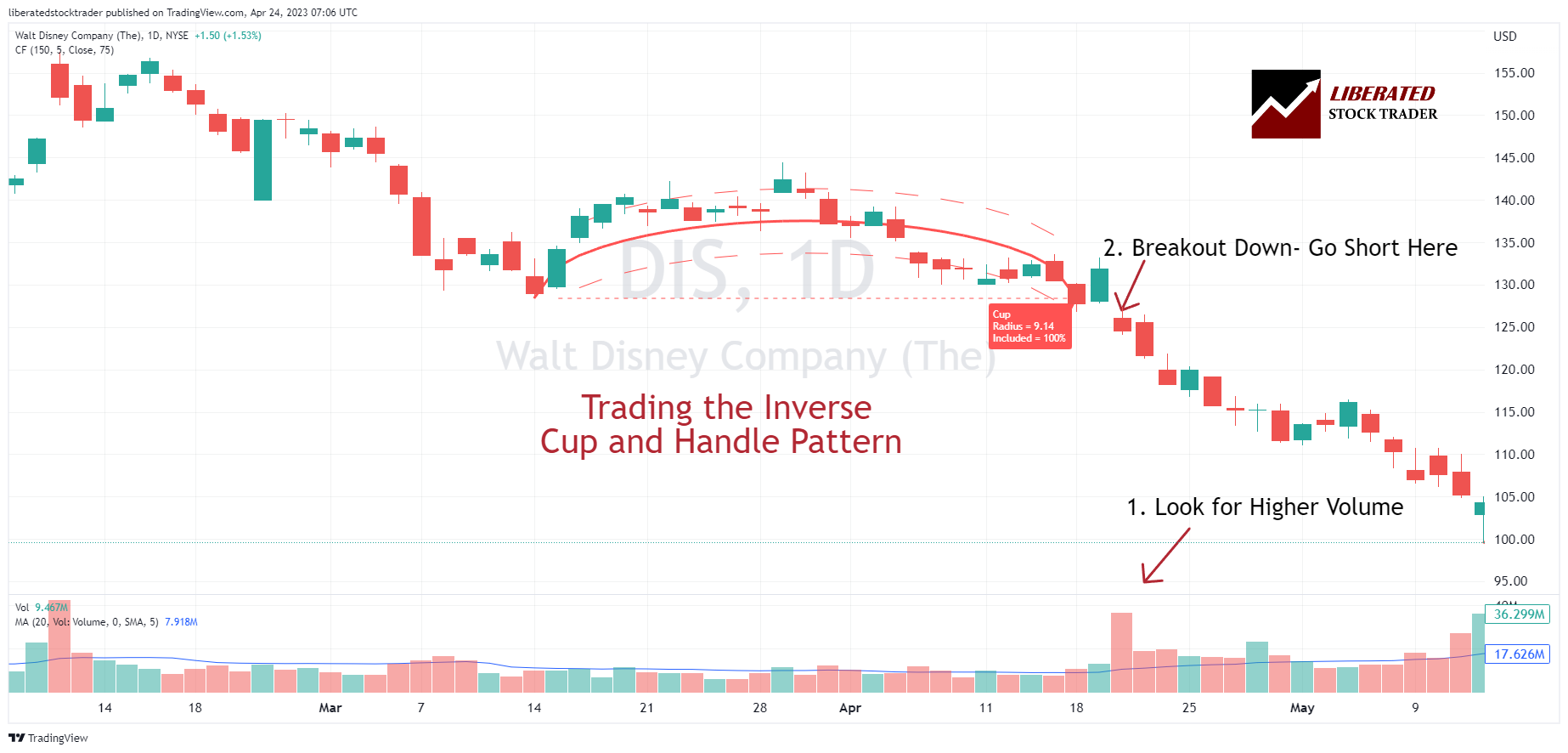
Example 1: Swing Trading a Cup and Handle (82% Reliable)
Identifying the cup and handle chart pattern can be challenging. First, observe a “cup” shape forming on the chart as the asset’s price rises and then retraces in a gentle U-shape over at least 30 trading days. Next, notice two declining trendlines forming, creating the “handle.” The handle should be less steep than the cup and persist for at least five days.
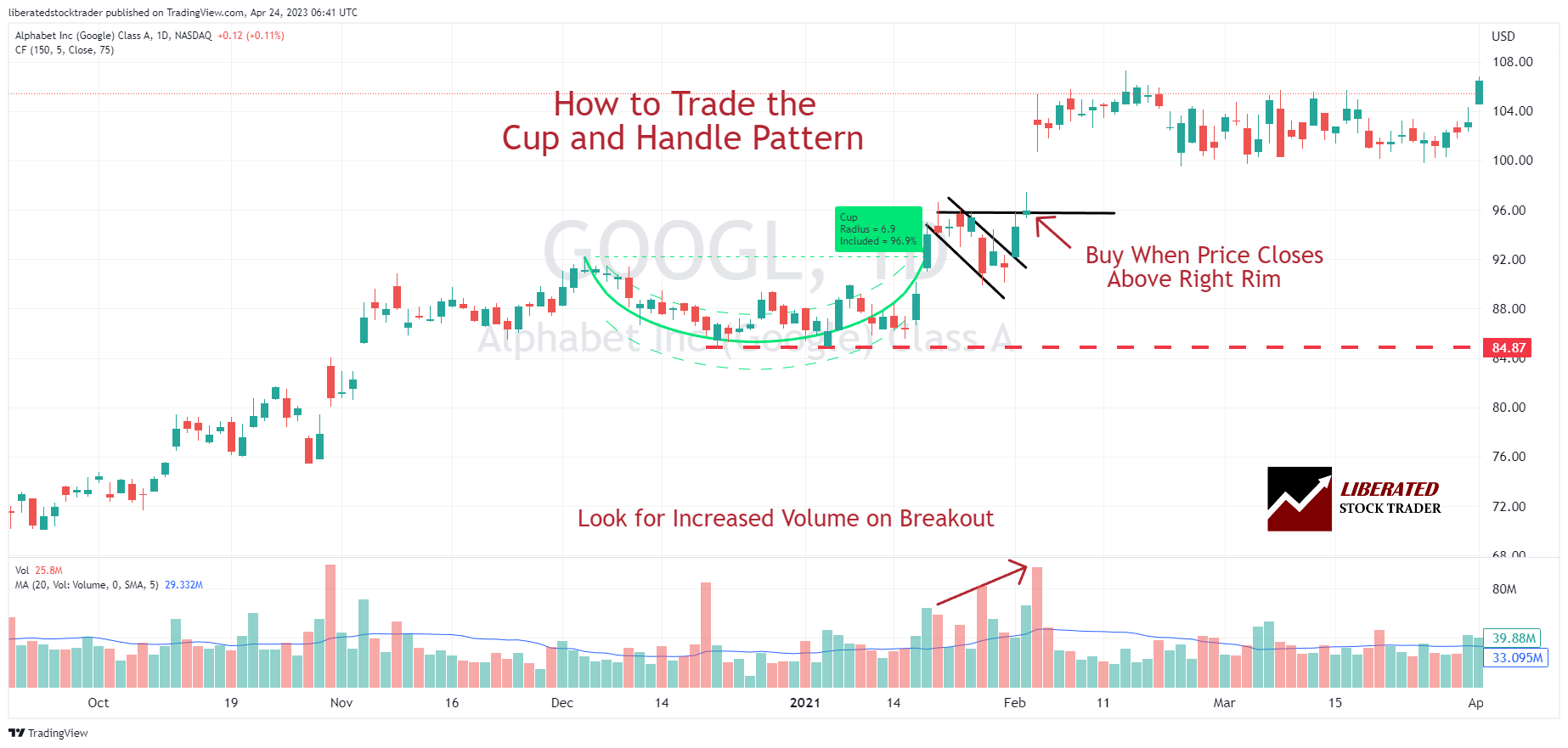
The breakout occurs when the asset’s price surpasses the highest point of the cup pattern, also known as the resistance line. This breakout often signals a strong uptrend. Confirming the breakout, traders seek a notable increase in trading volume. Following the breakout, anticipate a sustained upward price trend from several weeks to several months.
To help identify cup and handle patterns quickly and easily, use TradingView’s Cup & Handle Pattern Recognition tool. This tool helps you easily detect cup and handle patterns, making it much easier to identify high-probability trades.
Example 2: Swing Trading an Inverse Head & Shoulder (89% Reliable)
The inverse head and shoulders pattern occurs when a security’s price hits the bottom three times. The two troughs form the “shoulders,” while the third lower trough forms the “head.” This pattern suggests that the security price may soon start moving upward.
The inverse head and shoulders pattern has been a dependable indicator of potential reversals for decades. Its reliability stems from the requirement of three tests of the same resistance and a neckline break before it can be considered valid. This meticulous criterion enhances the accuracy and reliability of the signal.
Swing Trading vs. Day Trading
The difference between swing trading and day trading is timeframe and strategy. In swing trading, trades are held for a few days to a few weeks, while in day trading, trades are entered and exited within minutes to hours.
Swing trading focuses on capturing medium-term price movements and trends, while day trading aims to profit from high-frequency trading techniques and rely heavily on real-time data.
My thorough testing awarded TradingView a stellar 4.8 stars!
With powerful stock chart analysis, pattern recognition, screening, backtesting, and a 20+ million user community, it’s a game-changer for traders.
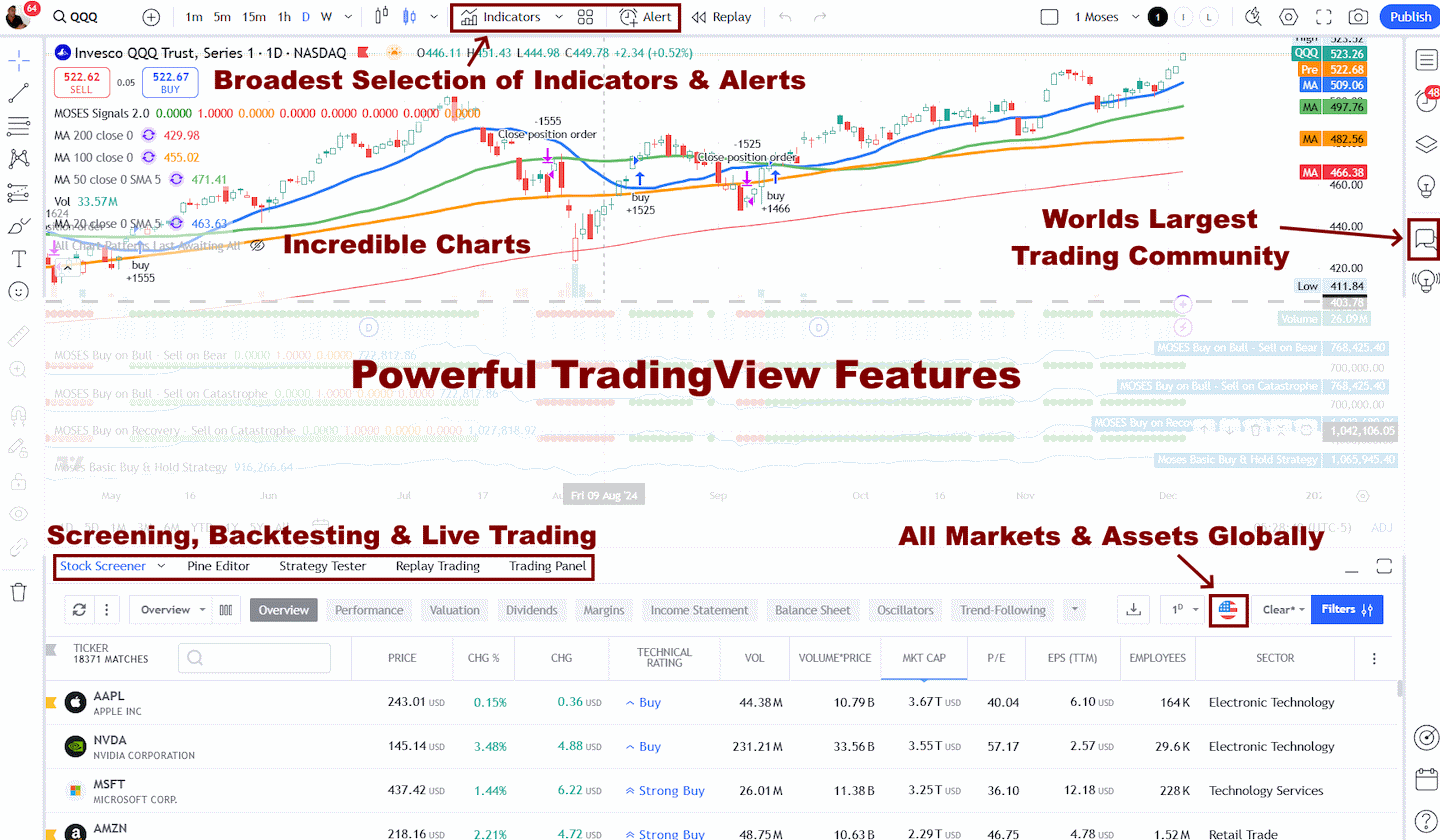
Whether you're trading in the US or internationally, TradingView is my top pick for its unmatched features and ease of use.
Explore TradingView – Your Gateway to Smarter Trading!
Common Swing Trading Strategies
Successful swing trading requires the implementation of proven strategies like moving average crossovers, breakouts, and reversals.
Moving Average Crossovers
This strategy involves using the crossover of different moving averages to identify buy or sell signals. For example, a shorter-term moving average above a longer-term moving average may indicate a bullish signal.
Breakout Trading
Traders look for stocks that are breaking out of a defined price range. When a stock breaks above resistance or below support levels, it may suggest a potential trend reversal.
Trend Reversal Trading
This strategy involves identifying stocks that have experienced a strong trend and may be ready to reverse direction. Traders look for signs of exhaustion in the current trend and enter trades anticipating a reversal.
Identifying Swing Trading Opportunities
Identifying potential swing trading opportunities requires combining technical analysis and automated market research. Here are some key factors to consider:
Technical Analysis: Look for stocks trading in an established range and have a history of bouncing between support and resistance levels.
Market Research: Utilize automated market research tools to scan the markets for potential swing trading opportunities. Focus on stocks with strong fundamentals, high volume, and relatively low volatility.
Fundamental Analysis
Evaluate a stock’s fundamentals, such as earnings growth, revenue growth, and financial health. Use this information to identify stocks with the potential for strong earnings growth or other catalysts that could cause a sudden price movement.
News Catalysts
Significant news events, such as earnings releases or mergers and acquisitions, can impact stock prices and present swing trading opportunities. Monitor real-time news events, economic reports, and other factors that could create opportunities for swing trading. Pay close attention to overnight market movements and intraday volatility to understand when breakouts might occur.
Candlestick Patterns
Analyzing patterns formed by individual candlesticks can provide insights into future price movements. We have tested over 25 candle patterns to prove which are successful.
Support and Resistance Levels
Identifying price levels where the stock has historically found support or faced resistance can help determine entry and exit points.
Sector Analysis
Analyzing specific sectors’ overall health and performance can help identify stocks with the potential for significant price movements.
Risk Management
Managing risk is essential for long-term success in swing trading; the key risk management techniques to consider are stop losses, position sizing, and risk/reward ratios.
- Setting Stop Losses: A stop loss is a predetermined price level at which a trader will exit a trade to limit potential losses. It helps protect against significant adverse price movements.
- Position Sizing: Determining the appropriate size of each trade based on available capital and risk tolerance is crucial. This ensures that no single trade has the potential to impact your overall portfolio significantly.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: It is essential to evaluate the potential reward against the potential risk of a trade. A favorable risk-reward ratio ensures that potential profits outweigh potential losses.
5 Swing Trading Tips for Beginners
If you’re a beginner looking to start swing trading, here are five essential tips:
- Educate Yourself: Learn about technical analysis, chart patterns, and indicators.
- Plan Your Trades: Develop a trading plan that includes entry and exit strategies, risk management techniques, and profit targets.
- Practice with Paper Trading: Before risking real capital, practice swing trading using virtual platforms to gain experience and test your strategies.
- Manage Risk: Set appropriate stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and determine position sizes based on your risk tolerance and account size.
- Stay Informed: Stay updated on market news, economic indicators, and sector performance to identify potential swing trading opportunities.
Avoiding Swing Trading Risks
While swing trading offers exciting opportunities, it’s important to be aware of potential risks, such as volatility, emotions, and a lack of strategy.
- Market Volatility: Rapid price movements can result in significant gains or losses. Use stop-loss orders and diversify your portfolio to manage risks.
- Emotional Trading: Emotions can cloud judgment and lead to impulsive trading decisions. Stick to your trading plan and avoid making decisions based on fear or greed.
- Lack of Proper Strategy: Without a well-defined trading strategy, it’s easy to fall into random trades. Develop a plan and stick to it consistently.
Remember, swing trading requires discipline, patience, and continuous learning. Adapting your strategies based on market conditions and constantly refining your skills is crucial.
Conclusion
Swing trading provides an exciting opportunity for beginner investors to profit from short-term price movements in the financial markets.
By understanding the basics, implementing proven strategies, and managing risks effectively, you can increase your chances of success as a swing trader.
