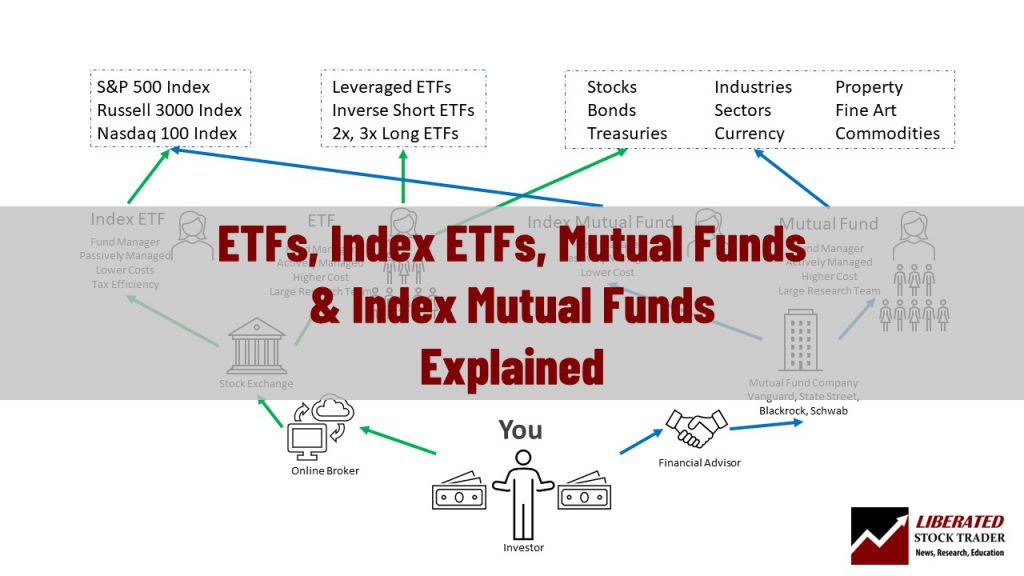
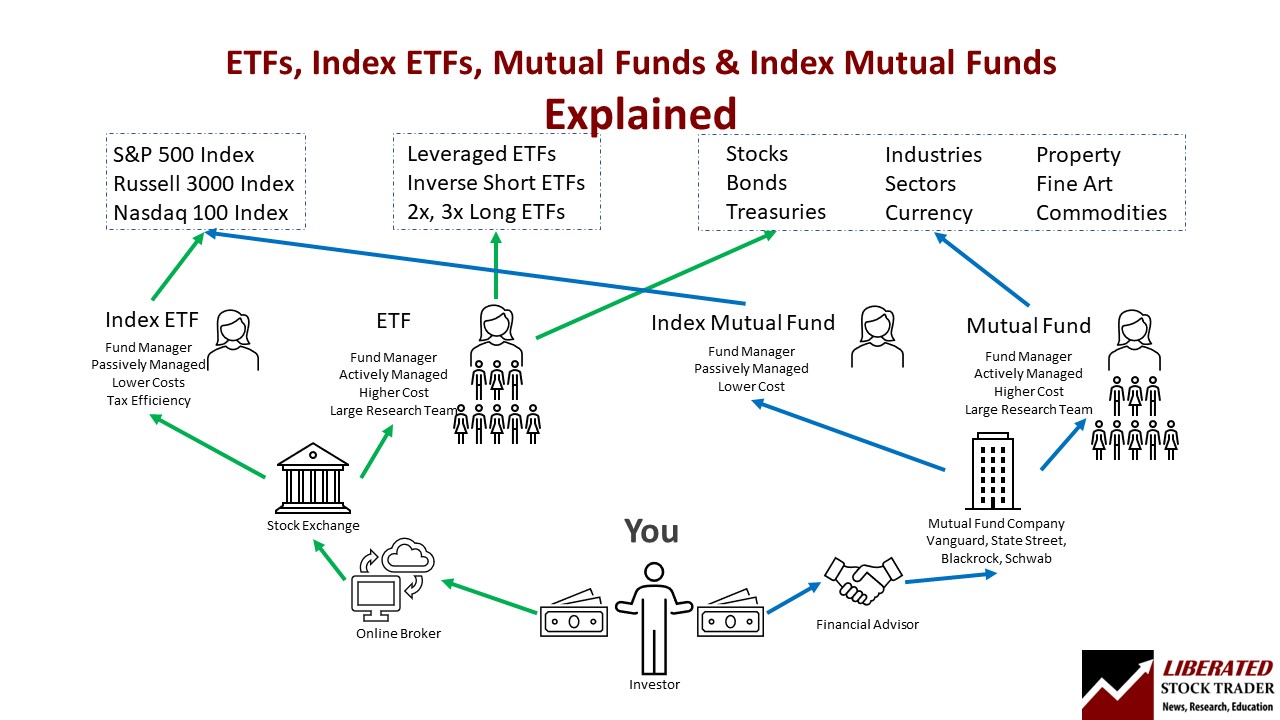
The difference between ETFs, mutual funds, and index funds is that ETFs trade like stocks on an exchange, and mutual funds are actively managed private investments.
To complicate things an index fund can be either an ETF or a mutual fund.
The world of index funds, ETFs, and mutual funds is surprisingly difficult to understand.
This article seeks to clarify the many questions posed by beginner and intermediate investors about investing in indices.
What is an ETF?
An exchange-traded fund (ETF) is a fund that is actively traded on a stock exchange during the trading day. An ETF can invest in an index, stocks, commodities, or derivatives. You can buy and sell ETFs in the same way you trade stocks.
Whatever the ETF invests in is the fund’s portfolio, which is actively traded on an exchange.
Although all ETFs have a named fund manager, many are considered passively managed funds, meaning they typically do not need a team of researchers to select stocks to try to beat the underlying benchmark’s performance. ETFs try to replicate the performance of an index, sector, or industry.
Actively managed ETFs exist and usually have a mix of assets that are not easily relatable to an underlying index.
ETF Chart Example
See More ETF Charts on TradingView
What is a mutual fund?
Mutual funds do not trade openly on an exchange; when you invest in a mutual fund, you make a fixed investment directly with the company for a price based on net asset value at the end of the trading day.
Mutual funds typically charge higher fees to pay the teams of researchers and fund managers who operate them to outperform the market.
Do mutual funds beat the market?
Yes, some mutual funds beat the market, but most do not. 82.5% of actively managed mutual funds in the USA failed to beat the market over the last ten years, according to the S&P Dow Jones Global SPIVA report. Over the last three years, only 32% of actively managed funds beat the market.
What’s the difference between ETFs and mutual funds?
ETFs are actively traded on stock exchanges with intraday pricing, whereas mutual funds are purchased directly from the issuer at the end of the trading day. ETFs have low minimum investment requirements, e.g., the cost of one share, but mutual funds typically have a fixed dollar investment requirement, such as $3,000.
While no-load mutual funds typically have no commissions for purchase or sale, they typically have higher maintenance, up to 3% per year, compared to passive ETF fees of 0% to 1%.
| ETF & Mutual Funds Differences | ETF | Mutual Fund |
| Index tracking | ✔ | ✔ |
| Actively managed | ✔ | |
| Passively managed | ✔ | |
| Fees | 0% – 0-6% | 1% – 3% |
| Traded like stocks on exchanges | ✔ | |
| Can be traded: | Intraday | End of day |
| Tax advantages | ✔ |
ETFs vs. Mutual Funds vs. Index Funds
The biggest difference between ETFs and mutual funds is the ability to trade an ETF in real-time on a stock exchange, compared to purchasing a mutual fund through an investment advisor with end-of-day prices. ETFs and Mutual funds can be index funds or have bespoke investment portfolios.
Which is better, ETF or mutual fund?
An ETF is better for investors seeking to keep fees low, avoid capital gains tax, and be able to liquidate their funds quickly during market hours. Mutual funds are better for investors wanting to invest in bespoke portfolios that attempt to outperform the stock market benchmark index.
What is an S&P 500 index fund?
An example of an S&P 500 index fund is the Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO). VOO is the largest index-tracking ETF globally, with $826 billion in assets under management, a 5-star Morningstar rating, and an expense ratio of 0.03%.
Is an ETF an index fund?
An ETF can be an index fund, but not all ETFs are index-tracking funds. Contrary to popular belief, both mutual funds and ETFs can track indexes. Both can be actively managed funds investing in different assets like stocks, bonds, or commodities.
Is an index fund a mutual fund?
An index fund can be a mutual fund or an exchange-traded fund (ETF). Think of an index fund as a portfolio that tracks an index and the ETF or mutual fund as different ways of buying shares of that index.
Are index funds safe?
Yes, index funds are safer than investing in individual stocks. Safety or risk is measured by Beta. Index funds have a Beta of 1, meaning they move in sync with the market, representing lower risk. A stock such as AMAT has a Beta of 2, meaning it fluctuates twice as much as the market, representing more risk.
What is the difference between ETF and index fund?
You can think of an ETF as the way a fund is operationally run, and an index fund is what that ETF invests in. If an ETF tracks an index, it is an index ETF fund; if a mutual fund tracks an index, it is an index-tracking mutual fund.
An ETF is a fund traded on an open exchange, whereas an index fund can be an ETF or a mutual fund.
The difference between an ETF and an index fund is the ETF is the vehicle for investing, and the index is the destination for the investment.
Are index funds and ETFs the same?
If you use an ETF to invest in an index, then yes, index funds and ETFs are the same thing. ETFs can be used to invest in an index, but they can also invest in different mixes of assets, like energy, metals, bonds, or treasuries.
Is SPY an index fund?
Yes, the SPY is an index fund operated by State Street. The SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust (SPY) is the third-largest ETF in the USA, with $414 billion in assets under management (AUM) and an expense ratio of 0.09% per year.
Is the S&P 500 an index fund?
No, the S&P 500 is a stock market index, not an index fund. The S&P 500 lists the 500 largest publicly listed companies on US stock exchanges. An index fund is a fund that will invest in the companies in the S&P 500 to match its overall performance.
The S&P 500 is an index, and an index fund is an ETF or mutual fund that invests in the S&P 500.
Is VTI an index fund?
Yes, VTI is an index fund. The Vanguard Total Stock Market Index Fund ETF (VTI) is the largest index-tracking ETF in the USA, with $1.3 trillion in assets under management. The VTI invests in the CRSP US Total Market Index, which is 4,000 companies representing the entire US stock market.
What is an index mutual fund?
An index mutual fund is a mutual fund that invests in an index. An example of an index mutual fund is the Vanguard 500 Index Fund Admiral Shares (VFIAX), which is offered as an ETF and a mutual fund.
Which is better, an index fund or an ETF?
An ETF that invests in an index is an index fund, meaning they are the same thing, so the answer to this question is that neither is better; they are just different.
Many ETFs are operated as index funds, so the question of which is better, an index fund or an ETF, cannot be answered. An index is what an ETF invests in. It’s like asking which is better, the car or the road; the ETF is the car, and the index is the road.
Are mutual funds and index funds the same?
Yes, a mutual fund that invests in an index means that a mutual fund and an index fund are the same. Although most index funds are operated as low-cost ETFs, many index-tracking mutual funds also exist.
How to invest in an S&P 500 index fund?
There are two ways to invest in an S&P500 index fund. You can use a broker and purchase the fund directly on the open market, or you can open an account directly with Vanguard or Schwab and invest directly with the investment firm.
Vanguard, State Street, and Black Rock provide the three largest S&P 500 index funds. To invest in an S&P 500 index fund, type the ticker VOO, SPY, or IVV into your stock brokerage account and click buy.
| Ticker | Largest S&P 500 Index Funds | Net Assets ($M USD) | Expense Ratio |
| VOO | Vanguard S&P 500 ETF | $821,279 | 0.03% |
| SPY | SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust | $411,595 | 0.09% |
| IVV | iShares Core S&P 500 ETF | $315,126 | 0.03% |
Can you beat the market with an index fund?
One of the best strategies for investing in index funds and outperforming the market is to avoid major stock market crashes. To avoid crashes, you must master technical analysis and have a rigorous, backtested system that has worked on all previous stock market crashes.
Beat The Market, Avoid Crashes & Lower Your Risks
Nobody wants to see their hard-earned money disappear in a stock market crash.
Over the past century, the US stock market has had 6 major crashes that have caused investors to lose trillions of dollars.

The MOSES Index ETF Investing Strategy will help you minimize the impact of major stock market crashes. MOSES will alert you before the next crash happens so you can protect your portfolio. You will also know when the bear market is over and the new rally begins so you can start investing again.
MOSES Helps You Secure & Grow Your Biggest Investments
★ 3 Index ETF Strategies ★
★ Outperforms the NASDAQ 100, S&P500 & Russell 3000 ★
★ Beats the DAX, CAC40 & EURO STOXX Indices ★
★ Buy & Sell Signals Generated ★
MOSES Helps You Sleep Better At Night Knowing You Are Prepared For Future Disasters
I have developed an ETF index investing system that beats the underlying benchmark index and lowers your risk at the same time. I achieve this by avoiding major stock market crashes.
