Stock float is the number of shares available to trade in the public market. This includes all shares held by institutional and retail investors and restricted stock owned by insiders.
Float can impact a stock’s trading volume, price movements, and volatility. If a company decides to issue additional shares through a secondary offering or stock split, the float will increase. If existing shareholders sell their shares or there is a buyback program in place, the float will decrease.
Learn how to research and trade the float.
What is Stock Float?
A stock float, also known as floating stock or simply “the float,” refers to the total number of a company’s shares that are available for public trading on the stock market. This does not include restricted shares, which company insiders or major stakeholders typically hold.
The size of a stock’s float can impact its volatility; stocks with a smaller float can be more volatile than those with a larger float because fewer shares are available for trading, leading to larger price swings with each trade.
The term “float” can refer to either the market or free float. The market float is the total number of outstanding (or available to trade) shares, including restricted and unrestricted shares. The free float is the number of freely traded or available-for-trade shares not held by company insiders, major shareholders, or other stakeholders with returning voting rights.
A stock’s float differs from its market capitalization and outstanding shares. Outstanding shares comprise all the stock a company issues, both in and out of the market. The float is part of the outstanding shares. Confusingly, a company’s balance sheet can list the outstanding shares as “capital stock.”
Market capitalization is the value of a company’s outstanding shares. Market capitalization does not determine a company’s value. A corporation’s assets can exceed the market capitalization. Similarly, the market cap can exceed the company’s value.
How to Calculate the Float of a Stock
To calculate a stock’s float, you need to know the number of outstanding shares and those insiders hold. To calculate the float, you subtract the restricted stock and the number of shares trading from the outstanding shares.
Float Formula:
Float = Outstanding Shares – (Restricted Stock + Shares Traded)
For example, if a company has 100 million outstanding shares and 10 million restricted shares, the float would be 90 million.
Restricted shares, such as preferred shares, are not available to the public. Management often sells restricted shares to company insiders or institutional investors. Once you understand market capitalization and how to calculate a stock’s float, you can accurately assess a company’s equity position in the public markets.
How to Trade Stock Float
When trading stock float, investors should pay attention to the overall market trend and whether a company is releasing new products or services. Positive news surrounding a company’s business outlook may cause its share price to rise due to increased demand for its shares. Additionally, if a stock’s float is low, it can increase volatility as large buys or sells have a more significant effect on the price.
Finally, traders should also research any news or developments related to a company’s float before making an investment decision. This will help them anticipate how float changes affect their trading strategy and position. By taking the time to understand stock floats, investors can gain an edge over other traders, take advantage of market inefficiencies, and capture potential profits.
Why Do Traders Use Float?
Float helps traders identify stocks that are likely to move in the near future, allowing them to capitalize on any sudden price changes. Additionally, float data can provide insight into the underlying demand for a stock. This knowledge can be used to gauge whether or not a stock has been fully discovered by the market yet and if it may be undervalued. Float is also used to identify stocks that have large institutional investors, as this can indicate a strong likelihood of future price movements.
My thorough testing awarded TradingView a stellar 4.8 stars!
With powerful stock chart analysis, pattern recognition, screening, backtesting, and a 20+ million user community, it’s a game-changer for traders.
Whether you're trading in the US or internationally, TradingView is my top pick for its unmatched features and ease of use.
Explore TradingView – Your Gateway to Smarter Trading!
Is Low Float in Stocks Good?
Yes, low float in stocks can be a good indicator of potential high-volume stock movements. This is because low floats tend to reduce the number of available shares that can be traded, which increases the average demand for each share and makes it easier for buyers to drive up prices. Additionally, when fewer shares are outstanding, any news or events that affect the stock will have a larger effect on the stock price. Low-float stocks are often highly volatile, so traders should ensure they understand the risks before investing in them.
How to Find the Float of a Stock
The easy way to find a stock’s float is to use a free stock screener such as FinViz. You can also try the hard way by checking the company’s Securities & Exchange Commission (SEC) filings. Those filings will tell you how much stock the company issues and what type it issues.
SEC filings can reveal insider ownership and show how much stock executives own. Executives selling stock can show you how much faith they have in the company. Insiders selling stock can be an indicator of problems at a company.
The SEC filings can show you how much stock the company owns and if the management is buying back stock. Stock buybacks can inflate share value and help investors make money.
The Easy Way to Find Stock Float Using Finviz
FinViz is a free stock screener that allows investors to search for stocks based on criteria such as market capitalization, sector, industry, and many other metrics. It can also be used to identify float size. To find a particular company’s float with Finviz, enter the ticker symbol in the search.
Using Finviz, you can easily find a stock’s float by opening a chart and looking at the information window.
3 Steps to Find the Float of a Stock with Finviz:
- Go to Finviz
- Click on any stock symbol
- Locate “Shs Float” or “Short Float” in the information windows below the stock chart.
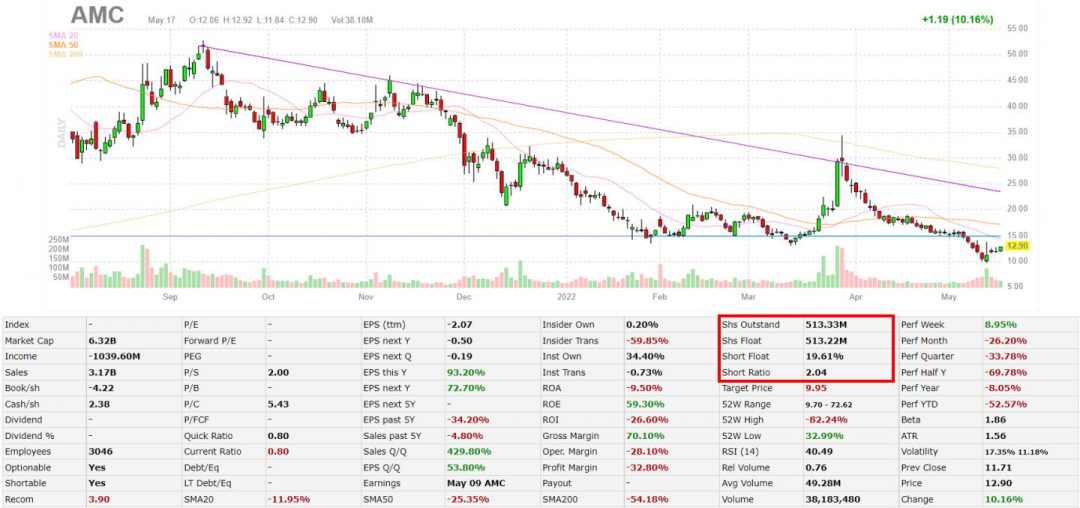
Start Screening for Float with Finviz Free
How to Screen for Float & Short Float Using Finviz
Finviz is one of the few stock screeners that allows you to filter on Float and Short Float for free.
3 Steps to Screen for Float & Short Float with Finviz:
- Go to Finviz
- Click on “Screener.”
- Select Filters “Description”
- Select “Float” or “Float Short” to get a list of stocks meeting your criteria.
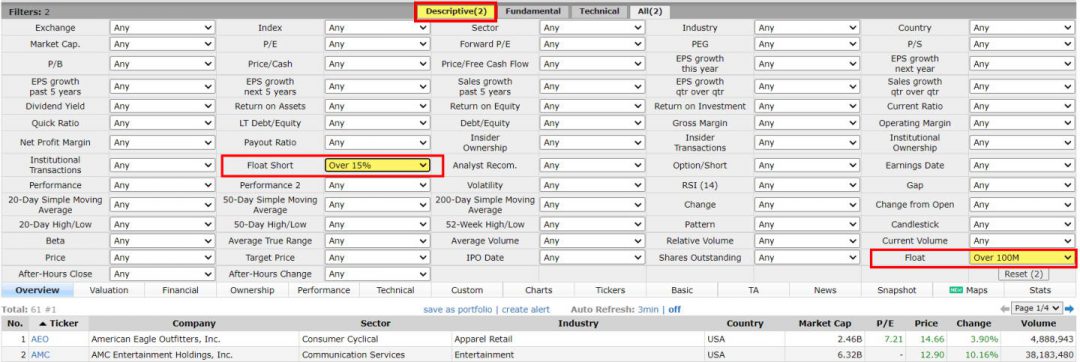
Start Screening for Float with Finviz Free
What is the Free Float of a Stock?
The free float of a stock is the number of shares that can be publicly traded. The size of the free float is important because it can show the ownership structure.
You calculate the free float by subtracting the market float from the shares outstanding. The resulting number is the free float. The float comprises the market float and the free float.
The size of the free float can show if large investors, insiders, and institutional investors such as pension funds, mutual funds, or hedge funds own large amounts of stock. A large float can indicate an investment analysts consider safe.
Investing In Stocks Can Be Complicated, Stock Rover Makes It Easy.
Stock Rover is our #1 rated stock investing tool for:
★ Growth Investing - With industry Leading Research Reports ★
★ Value Investing - Find Value Stocks Using Warren Buffett's Strategies ★
★ Income Investing - Harvest Safe Regular Dividends from Stocks ★

"I have been researching and investing in stocks for 20 years! I now manage all my stock investments using Stock Rover." Barry D. Moore - Founder: LiberatedStockTrader.com
What is the Market Float of a Stock?
The market float is the amount of stock trading in the markets. It is calculated by subtracting the trading volume from the free float.
The market float is hard to determine because it changes whenever stock trades. A high market float can show low demand for a stock, while a low market float can indicate high demand.
Market float can show how vulnerable a company is to a takeover. If a company’s market float is high, an outsider can easily take over by buying up shares. Large amounts of outstanding shares outside the market indicate other owners who can block a buyout.
What is the Short Float?
Short float is the percentage of a stock’s market float that is shorted. When somebody shorts a stock, she borrows the shares from a broker or platform. The borrower is betting she can make enough money from short-selling the stock to pay the broker and profit.
Brokerages report the number of shares sellers are shorting twice a month. The short float is the amount of a company’s stock that is being shorted. Major exchanges, platforms, and financial news outlets post those figures online.
You can use a short interest ratio to identify overly shorted stocks. The short interest ratio is the number of shares held short divided by the average daily trading volume. An overly shorted stock indicates that traders think a stock price will fall. The short float is important because it shows traders’ faith in that stock.
Do Shorts Increase the Float of a Stock?
Shorts do not increase a stock’s float because company management controls the float and cannot be externally influenced by short sellers.
Shorts can increase the short float on a stock because the short float is a financial calculation. Short float is simply the percentage of the float being shorted by short-sellers.
The market float is the number of shares trading, and the free float is the number of shares in private hands. Shorts cannot increase the number of shares trading. However, a high short-interest ratio can convince some to sell shares and increase the market float.
Warren Buffett’s Float
It would be best not to confuse the stock float with Warren Buffett’s float definition. Buffett and other value investors use the term float to describe a company’s excess cash. Companies like Berkshire Hathaway (BRK.B) use float to pay for expansion and acquisitions.
Buffett’s definition of float often refers to companies with regular sources of cash, such as subscription payments. Amazon (AMZN) generates float from Amazon Prime subscriptions, for example.
A stock’s float is important because it shows the demand for a stock. Float can also show the company’s ownership structure and indicate changes in ownership. All investors must examine float because it can show you where a stock is going.
The Importance of the Float in Trading
It is important to remember that the float is not constant and can change over time. For example, a company may buy back its stock, which would reduce the float. Or, a company may issue new shares, which would increase the float.
Float is just one factor to consider when trading stocks. It is important to do your research before making any investment decisions.
FAQ
What is the best software to find stock float?
The best software to find short-float and low-float stocks is Finviz. Finviz allows traders to quickly sort stocks by their short float, total float, and short ratio. Additionally, it offers a comprehensive platform with charts, news, and market data from all US exchanges.
What is stock float?
Stock float refers to the number of shares available for trading by the public. It's calculated by subtracting closely held shares, including those owned by insiders, employees, and major long-term shareholders, from the total shares outstanding.
Why is stock float important?
Stock float is crucial to day traders, as it indicates the supply of shares available for trading. A lower float can mean higher price volatility, as fewer shares are available for trading.
What is considered a low float?
Typically, a company with under 15 million shares in its float is considered a low float. However, this isn't a hard rule and can vary based on the industry and market conditions.
What is a high-float stock?
A high-float stock is one with many shares available for public trading. High-float stocks often have more price stability due to their larger supply of shares.
Does stock float change?
Yes, the stock float can change. It increases when the company issues more shares, or closely-held shares become available for trading. It decreases when the company buys back its shares.
What does a small stock float indicate?
A small stock float suggests fewer shares are available for public trading. This can lead to higher price volatility, especially if the demand for the shares outweighs the supply.
How does stock float affect stock price?
Stock float can impact price volatility. Stocks with low float can experience significant price swings, while high float stocks typically show more price stability and lower bid-ask spreads.
Is it better to invest in low or high-float stocks?
Neither is inherently better—it depends on your risk tolerance. Low-float stocks can have high volatility, offering the potential for large gains (or losses), while high-float stocks typically offer more stability.
What is float percentage?
Float percentage is the portion of total shares available for public trading. It's calculated by dividing the float by the total shares outstanding and multiplying by 100.
What does negative stock float mean?
Negative stock float is a rare occurrence and typically results from a miscalculation. In theory, it can occur if more shares are short-sold than are available in the float.
What is the difference between shares outstanding and float?
Shares outstanding refers to all shares a company has issued, while float only includes those available for public trading.
What is restricted stock vs. float?
Restricted stock refers to shares held by insiders and cannot be traded due to regulations. These are not included in the float.
How do share buybacks affect the float?
Share buybacks reduce the number of shares in the float, as the company effectively removes shares from public trading.
What is a float rotation?
A float rotation is the process of moving shares between public and restricted markets, increasing or decreasing the total number of shares available to traders. This can be done intentionally as part of a company's strategy or occur unintentionally due to miscalculations. Float rotations are typically rare occurrences.
What is a float lock-up?
A float lock-up refers to a period post-IPO during which insiders cannot sell their shares, effectively reducing the float.
What is the relationship between float and liquidity?
The larger the float, the higher the stock's liquidity, as more shares are available for trading.
What is a float-adjusted market cap?
A float-adjusted market cap takes into account only the value of shares available for public trading rather than the total shares outstanding.
Can dividends affect the float?
Dividends do not affect the float, as they do not change the number of shares available for public trading.
