Hawks and doves are distinct camps in economics regarding fiscal policy.
Hawks favor tight monetary policy (high interest rates, low government spending), while doves prefer loose policy (low interest rates, high government spending).
This difference is usually associated with the goal of either controlling inflation or encouraging economic growth.
Find out how the Federal Reserve’s decisions impact not only US markets but the entire globe’s wealth.
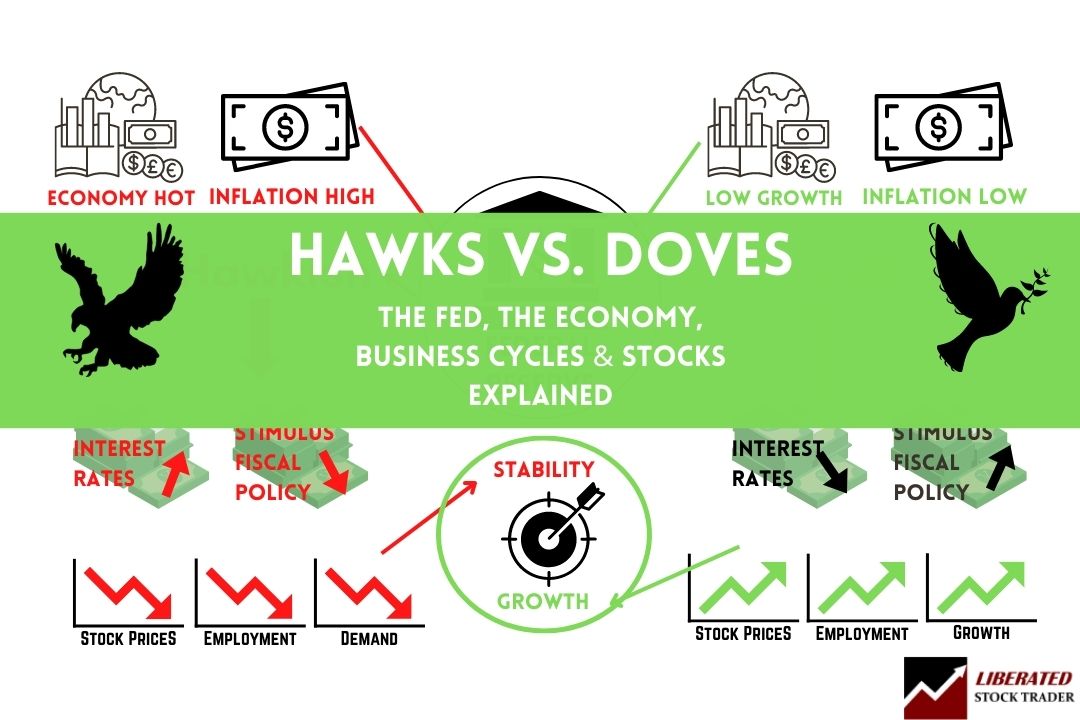
Differences: Hawks and Doves
Hawkish vs. dovish refers to the policy stance of the Federal Reserve governors. Hawks are prepared to swoop down to restrict growth in an overheating economy. Doves want economies to fly by reducing interest rates to boost investment, employment, and growth.
Hawks tend to worry more about inflationary pressures, while doves are more concerned with ensuring economic growth. This hawk-dove split can explain how the Fed may act in any given situation.
Key Takeaways
- The Federal Reserve has been a key player in the American economy since its inception.
- The Fed comprises influential doves and hawks who have shaped its policies.
- Doves favor loose monetary policy, while hawks prefer tighter conditions
- The goal of the Federal Reserve is economic stability and growth
- Hawks are concerned about inflationary pressures and stopping asset bubbles that impact stability.
- Doves focus on improving economic growth and employment.
Hawks vs. Doves in the Federal Reserve
Dovish and hawkish are terms used to describe the monetary policies of the United States Federal Reserve and other central banks. A dovish stance means that the Federal Reserve leans towards lower interest rates and is more willing to engage in quantitative easing.
In contrast, a hawkish stance indicates that the Fed may raise interest rates or tighten monetary policy to control inflation.
A dovish position may also be characterized by rhetoric from central bankers suggesting an expansionary fiscal agenda, such as growth spending on infrastructure and clean energy. In contrast, a hawkish outlook may include high-level actions such as raising taxes or reducing government spending to bridge budget deficits.
Regardless of which stance is taken, both have important implications for national economic performance and, thus, should not be taken lightly.
In short, the Fed’s dovish stance seeks to maintain low interest rates and a steady economy. Conversely, a hawkish stance seeks to raise interest rates to control inflation and slow economic growth.
Tools used by doves & hawks
The Federal Reserve’s primary tools for implementing either a dovish or hawkish policy are open market operations and interest rate changes.
Open market operations involve buying and selling US Treasury notes to change the money supply. By altering these parameters, the Federal Reserve can affect macroeconomic indicators such as GDP growth, inflation, unemployment rates, and consumer spending.
Charting Economic Indicators
Using leading financial charting and research software like TradingView, we can visualize the key economic indicators the Federal Reserve uses to make policy decisions.
Trading excels in monitoring economic indicators, seamlessly connecting to the Federal Reserve’s FRED database. The platform boasts a comprehensive array of financial charts encompassing key metrics like Inflation, Interest Rates, GDP, and Employment.
Inflation Rate Chart
Controlling inflation is the primary economic goal of the Federal Reserve. The consumer price index (CPI) measures the cost of a basket of goods and services used to track inflation in a given country.
Get Economy Charts & Indicators Free on TradingView
In the US, the unadjusted Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers is based on a market basket of goods and services. This includes Food (14%), Energy (8%), Commodities Less Food & Energy (21%), and Services Less Energy (57%). The Services Less Energy category is divided into Shelter (32%), Medical Care Services (7%), and Transportation Services (6%).
Interest Rate Chart
Interest rates are used to control the cost of borrowing money. The Federal Reserve sets a target rate for federal funds, the rate banks use when loaning money to each other. This affects the prime rate, which banks offer to their best customers. It also affects mortgage rates and credit card rates.
Get Economic Indicators Free on TradingView
Debt to GDP Charts
GDP (Gross Domestic Product) is the total value of all goods and services produced in a country over a given period. It measures economic growth and indicates an economy’s overall health. Most governments report GDP quarterly, and it can be used to compare different countries’ performance.
Get Charts & Indicators Free on TradingView
Unemployment Indicators
The US Unemployment rate measures the number of people in the labor force who are unemployed. It’s an important economic indicator that can affect consumer spending and other aspects of the economy. The US Bureau of Labor Statistics releases monthly reports on unemployment rates for all states and national data.
Get Economy Charts & Indicators Free on TradingView
Economy & Business Cycles Dictate the Feds’ Policy
In 2008, during the global financial crisis, the bubble burst in the property market, causing homelessness, increased unemployment, a stock crash, and consumer panic. These factors forced Central Banks into a strong dovish policy of injecting capital into the economy through stimulus, fiscal policy, and reduction in interest rates.
Infographic: Hawks vs. Doves Explained
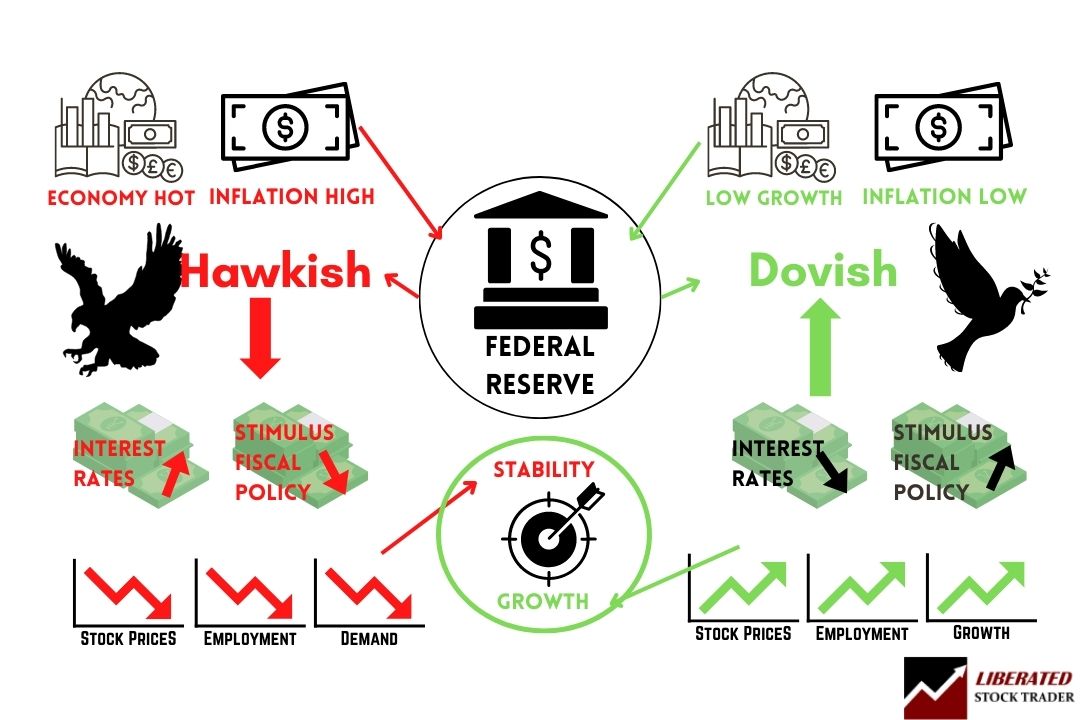
While this dovish policy saved the economy, many argue it caused an overheated economy, leading to the 2022 crash.
When the economy is running too hot, high inflation, labor shortages, and asset bubbles in cryptocurrency, property, and stocks affect economic stability. To counter overheating, the Federal Reserve and other central banks must adopt hawkish policies to slow growth and cool the economy.
Hawks, doves, and business cycles
Hawkish and dovish refer to the monetary policies of the Federal Reserve, which are used to influence the business cycle. A hawkish stance indicates that the Fed may raise interest rates or tighten monetary policy to control inflation and economic growth.
This type of policy is often used during periods of economic prosperity when GDP growth is high and inflationary pressures are rising. A hawkish stance aims to keep inflation in check by controlling wages and reducing consumer spending.
Conversely, a dovish stance means that the Federal Reserve is biased towards lower interest rates and is more willing to engage in quantitative easing. This policy is usually adopted at the bottom of the business cycle, during economic downturns when GDP growth slows and unemployment rises. Its goal is to encourage investment and stimulate job growth by making it easier for businesses to borrow money at lower interest rates. By lowering interest rates, the Fed hopes to incentivize consumers to spend more and businesses to invest more in their operations.
My thorough testing awarded TradingView a stellar 4.8 stars!
With powerful stock chart analysis, pattern recognition, screening, backtesting, and a 20+ million user community, it’s a game-changer for traders.
Whether you're trading in the US or internationally, TradingView is my top pick for its unmatched features and ease of use.
Explore TradingView – Your Gateway to Smarter Trading!
Hawks, doves, and the stock market
Hawkish and dovish policies can have a significant impact on the stock market. When interest rates rise, monetary policy tightens, restricting business access to credit and stifling profits and the capital needed for expansion and innovation. This can cause stock prices to fall as investors look to other investments with less risk.
Conversely, borrowing is more affordable for businesses and individuals when the Federal Reserve adopts a dovish stance and lowers interest rates. This can lead to increased demand for certain stocks as businesses have more access to credit, and investors look for companies with strong fundamentals. When a dovish policy is in place, it can increase stock prices as companies can expand and grow more easily.
Why does the Fed change its stance between hawkish and dovish?
Depending on how different macroeconomic indicators develop over time, the Federal Reserve might sometimes adopt a combination of hawkish and dovish policies. For instance, if inflation starts increasing while GDP growth remains low, combining both policies could reign in inflation without stifling economic recovery efforts.
Similarly, if GDP growth accelerates while inflation remains low, then dovish policies could be implemented to avoid any potential overheating without stifling economic activity too much.
Why is understanding dovish and hawkish policy important?
Ultimately, understanding the differences between hawkish and dovish stances will help investors determine what type of monetary policy the Federal Reserve may adopt at various points during an economic/business cycle. This can be beneficial for making smart investment decisions as it will provide clues as to whether it’s better to invest in stocks or bonds depending on the environment within each business cycle phase.
Pros and cons of Hawks & Doves
Pros: Hawkish federal policy
The primary pro of a hawkish Federal policy is that it can help mitigate the risk of inflation or let the air out of asset bubbles. The Federal Reserve can limit spending and reduce aggregate economic demand by raising interest rates and tightening the money supply. This will create an environment where goods, services, and wages become cheaper by decreasing consumer spending.
Cons: Hawkish federal policy
A hawkish Federal policy can have some negative consequences, as increasing interest rates makes it more difficult for businesses to borrow money and invest in new projects. This can decrease investment spending, slowing economic growth and job losses.
Additionally, higher interest rates can negatively affect consumer spending. People must pay higher interest rates to borrow money or buy property, which reduces their disposable income. This can lead to a decrease in consumption and slow economic growth even further.
Pros: Dovish federal policy
The pros of a dovish Federal policy are that it is designed to help stimulate economic growth. By lowering interest rates and increasing the money supply, businesses can more easily borrow money and invest in new projects. This will lead to job creation and increased consumer spending, which can help to stimulate economic growth.
Cons: Dovish federal policy
The cons of a dovish Federal policy are that it can lead to an increase in inflation. Increasing the money supply makes it easier for businesses and consumers to borrow and spend more. This can cause a surge in aggregate demand, driving up the prices of goods and services. Additionally, if too much money is pumped into the economy, it can lead to an imbalance between supply and demand, which can cause asset bubbles.
Overall, understanding the differences between hawkish and dovish policies can benefit investors by providing clues as to the type of environment in each business cycle phase. This can help them make more informed investment decisions and potentially capitalize on opportunities created by shifts in Federal policy.
Example: How doves or hawks affect economic decisions
There are two distinct attitudes when it comes to economic decisions: being dovish or hawkish. In a dovish scenario, the government or other decision-makers intend to keep inflation rates low and focus on reducing unemployment. They are typically willing to use expansionary policies such as monetary easing and tax cuts to achieve this.
A hawkish attitude is one in which the decision makers take a more restrictive approach towards the economy, for example, by increasing interest rates and keeping tight budget control. This can be beneficial in controlling inflation and preventing financial instability but can come at the cost of reduced economic growth.
Ultimately, dovish or hawkish decision-makers use various economic tactics to foster growth and stability.
Why do doves and hawks never agree?
Opinions vary on when economic policy should be dovish or hawkish. Those who lean toward a more dovish approach often argue that monetary policy should be more flexible and forgiving when shocks occur in the financial system. To combat weak growth, they believe a central bank should use low interest rates and other forms of quantitative easing to stimulate the economy.
On the other side, hawks stress the importance of fiscal or monetary discipline during economic booms and view inflationary pressure as an immediate threat to economic stability. Therefore, they advocate for higher interest rates and less government interference to keep inflation in check. Ultimately, whether an economy benefits from an explicitly dovish or hawkish stance will depend on its unique circumstances at any given time.
Famous doves and hawks in Fed history
Throughout its history, the Federal Reserve System has seen its share of policy debate between those advocating for a “dovish” approach, such as easing economic conditions to place downward pressure on inflation and growth, and those who hold a more “hawkish” set of views, including raising interest rates to put an end to high levels of spending and inflation.
Perhaps the most famous dove was then-Fed Chairman Alan Greenspan, who assumed office from 1987 until 2006 and is credited with keeping the economy on track during some of the toughest economic times in US history. However, Greenspan’s dovish approach and vast deregulation ultimately led to the 2008 financial crisis.
On the other hand, current Fed Chair Jerome Powell is considered hawkish for his risk-averse policymaking approach and emphasis on fiscal responsibility. Regardless of where they fall on the spectrum of opinion, these prominent individuals have all contributed to furthering our understanding of how monetary policy affects the American economy.
Summary: Doves vs. hawks
Regarding the Federal Reserve, there are two main camps: doves and hawks. Doves prioritize economic growth and job creation, while Hawks emphasize keeping inflation in check. Both approaches have pros and cons, so there is often debate about which is better for the economy. Some of the most famous members of the Fed have been doves or hawks, depending on their views at the time. Today, several members of the Fed Board lean either way.
In short, doves favor easier monetary policy, while hawks prefer tighter conditions. Both have pros and cons, so there are different views on whether being dovish or hawkish is better for the economy.
As you continue investing, learning more about economics and fundamental analysis is important to make informed decisions about investing your money. With our professional investing training course, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a successful investor.
Investing In Stocks Can Be Complicated, Stock Rover Makes It Easy.
Stock Rover is our #1 rated stock investing tool for:
★ Growth Investing - With industry Leading Research Reports ★
★ Value Investing - Find Value Stocks Using Warren Buffett's Strategies ★
★ Income Investing - Harvest Safe Regular Dividends from Stocks ★

"I have been researching and investing in stocks for 20 years! I now manage all my stock investments using Stock Rover." Barry D. Moore - Founder: LiberatedStockTrader.com
FAQ
What is the best software for economic indicators?
TradingView is perfect for tracking economic indicators. TradingView connects to the Federal Reserve's FRED database and offers an extensive library of financial charts, including Inflation, Interest Rates, GDP, and Employment.
What do the terms “doves” and “hawks” mean?
Doves and hawks are terms used to describe the economic policy attitudes of central bankers. Doves are typically more concerned with unemployment and willing to tolerate some inflation. Conversely, Hawks prioritize controlling inflation, even if it means higher interest rates and slower economic growth.
How does a dove’s approach affect the economy?
A dove's approach, which is more tolerant of inflation and focuses on employment and growth, can lead to lower interest rates. This stimulates spending and investment, potentially leading to economic growth. However, it can also lead to higher inflation rates.
What impact do hawk’s have on the economy?
Hawks' focus on controlling inflation often results in higher interest rates. While this can slow down economic growth and increase unemployment in the short term, it helps keep inflation in check, providing long-term economic stability.
Can a central bank be both dovish and hawkish?
Yes, a central bank can adopt both stances depending on the economic situation. The balance between dovish and hawkish policies can shift over time based on economic indicators like inflation, unemployment, and GDP growth.
How do dovish and hawkish stances influence stock markets?
With lower interest rates, Dovish policies generally stimulate stock markets as borrowing becomes cheaper, encouraging investment. Hawkish policies, conversely, can cause markets to contract as higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive.
What are the risks of a dovish monetary policy?
While dovish policies can boost economic growth, they can also lead to high inflation rates. If left unchecked, this could devalue currency and erode purchasing power.
What are the dangers of a hawkish monetary policy?
Hawkish policies can control inflation effectively, but they risk slowing economic growth and increasing unemployment due to higher interest rates.
What indicates a dovish shift in policy?
Indicators might include cuts in interest rates, increased government spending, or statements from central bankers emphasizing the importance of economic growth and employment over inflation control.
What are signs of a hawkish turn in policy?
Signs could include hikes in interest rates, reduced government spending, or statements from central bankers stressing the need to control inflation, even at the expense of slower growth.
Why do investors care about doves and hawks?
Investors care because these stances influence economic conditions, affecting investment returns. Dovish policies can boost stock markets, while hawkish policies lead to market contraction.
How does a dovish or hawkish stance affect my investments?
Your investments may increase in value during dovish periods due to stimulated economic growth. Conversely, during hawkish periods, your investment value may decrease due to slowed economic growth.
How can I adjust my investment strategy based on dovish or hawkish policies?
During dovish periods, consider investing in growth-oriented assets. It might be wiser to focus on more stable, inflation-resistant investments, such as bonds in hawkish periods. Additionally, diversifying your portfolio is generally a good idea regardless of the economic environment.
What is the current stance of the Federal Reserve?
The Federal Reserve's stance can change based on current economic conditions. Refer to the latest Federal Reserve meeting minutes or public statements to get up-to-date information.
How often do central banks review their policy stance?
Central banks monitor economic conditions, but formal reviews typically occur during regular policy meetings. Depending on the bank, these can be monthly, quarterly, or at other intervals.
Can I predict the future policy stances of central banks?
While it's impossible to predict with certainty, you can make educated guesses based on economic indicators and public statements from central bankers. However, always be prepared for unexpected changes.
