Earnings Per Share (EPS) is one of the most important ratios to assess a company’s profitability.
EPS measures a company’s profitability and gives investors an idea of how much profit each share of stock represents. However, just looking at the current EPS alone is not enough to fully understand a company’s potential.
“The acceleration in the growth of earnings per share (EPS) is the foundation of selecting high-performing growth stocks.”
I will explain how experienced investors use EPS and show evidence of why growth and EPS acceleration are the core of a successful growth investing strategy.

What is EPS
Earnings Per Share (EPS) is a financial ratio that indicates a company’s profitability on a per-share basis. It’s a measure calculated by dividing the company’s net income, less any dividends on preferred stock, by the number of outstanding ordinary shares. This ratio gives investors and analysts an insight into the company’s profitability from the shareholders’ perspective.
The primary purpose of EPS is to provide investors with a standardized way to compare the financial performance of different companies within the same sector or industry. Companies with higher EPS are often seen as more profitable and a better investment. However, to make an informed decision, it is essential to consider EPS in the context of other financial metrics, such as return on equity (ROE) and price-to-earnings ratio (P/E).
Key Takeaways
- Earnings Per Share (EPS) is a crucial indicator of a company’s profitability.
- There are three ways to calculate EPS: Basic EPS, Diluted EPS, and Adjusted EPS.
- EPS compares the financial performance of different companies in the same sector or industry.
- EPS Analyst Estimates: Financial analysts provide forecasts of a company’s future earnings, helping investors anticipate the company’s near-term performance. However, these predictions are often inaccurate.
- EPS Surprises: Significant differences between a company’s reported EPS and the estimates set by analysts can considerably impact a company’s stock price. Positive surprises generally lead to an increase in stock price, while negative surprises can result in a decline.
- EPS Acceleration indicates that a company’s EPS growth rate has increased over time, which can be interpreted as a sign of improving financial health and performance. This can be beneficial for investors as it suggests potential for long-term returns. When assessing whether or not a company has had to accelerate EPS, investors should look at the quarterly and
Investors view a high EPS positively, but EPS growth and acceleration rate are the cornerstones to finding excellent growth stocks.
What Does a High EPS Mean?
A company with a high EPS can be interpreted as being more profitable and is typically seen as a positive sign to investors. This indicates that the company is well-managed and has generated strong profits from its operations. Thus, companies with high EPS often attract higher valuations from investors due to their perceived long-term potential for growth and profitability.
What Does a Low EPS Mean?
A company with a low EPS may indicate that it is not operating as efficiently and could be underperforming compared to peers in its sector. In such cases, investors may consider other metrics, such as ROE or P/E ratios, when making investment decisions. Companies with consistently low EPS should also be closely monitored for potential red flags such as inefficient operations or weak management.
What is a Good EPS?
A good EPS is highly dependent on the sector and industry in which a company operates and the size of the EPS compared to the share price. Generally speaking, higher EPS ratios are considered more desirable and indicative of a well-managed company with strong profitability potential.
A Theoretical Practical Example of a Good EPS
If the share price of company A is $10 and the EPS is $1.2, then the EPS is 12% of the share price (1.2/10). If the share price of company B is $20 and the EPS is $1.5, then the EPS is 7.5% of the share price (1.5/20). In this case, the EPS for company B is higher in dollar terms, but company A has a higher EPS ratio and is viewed more favorably by investors.
A Practical Example of a Good EPS
Consider a technology company like Apple Inc., which has consistently demonstrated a high EPS. As of 2023, its trailing twelve-month (TTM) EPS was $7.13. This high EPS reflects Apple’s strong profitability and efficient operations. It signals to investors that Apple can generate substantial earnings per share of stock; hence, it’s a more profitable investment than other companies with a lower EPS.
Where to Find the EPS
The EPS is reported in a company’s income statement, usually under the heading of earnings per share or net income per share. The EPS is also typically reported on a company’s annual report and stock exchange filings.
The EPS is most easily found online in stock charting software like TradingView or stock research and screening software like Stock Rover.
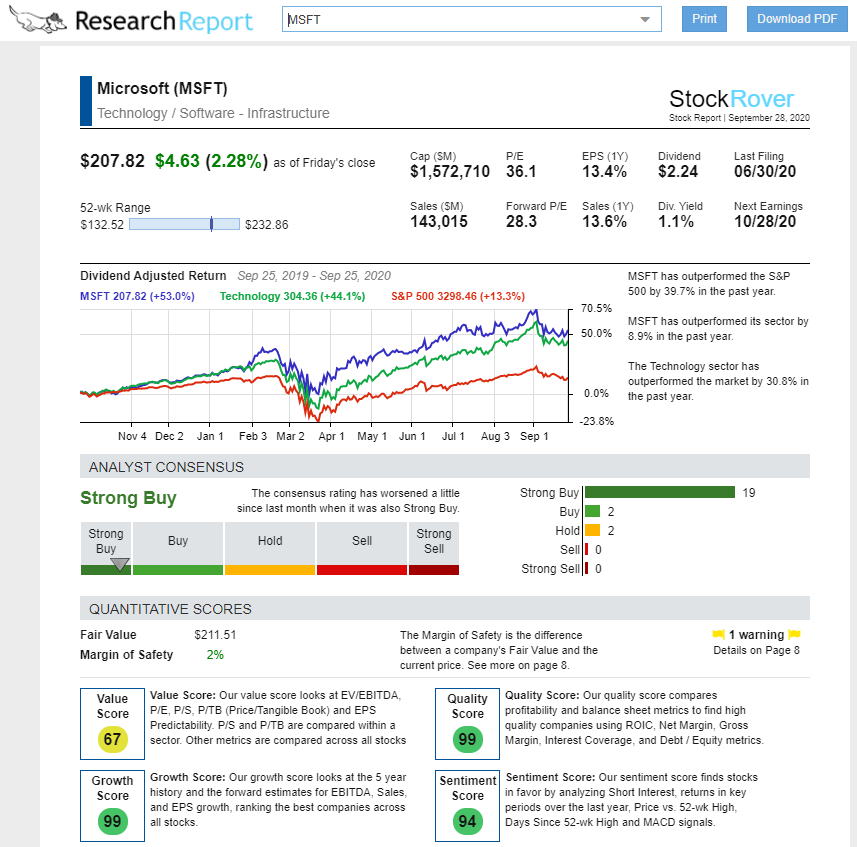
Find EPS & Financials in Stock Rover Research Reports
Using EPS in Stock Charts
Investors often use Earnings Per Share (EPS) in stock charts to analyze a company’s performance over time and make informed investment decisions. Stock charts with EPS information allow investors to visually compare a company’s earnings against its stock price movements.
The EPS line is typically plotted on the stock chart as a series of data points connected by a line representing the EPS values for different reporting periods. This line allows investors to see how a company’s earnings have changed over time.
An upward-trending EPS line in a stock chart is usually a positive sign, indicating that the company’s earnings are increasing. Conversely, a downward-trending EPS line may signal a company’s declining profitability.
See Apple Inc.’s Chart & Financials on TradingView
How Investors Use EPS
Investors use EPS to evaluate a company’s profitability. Generally speaking, companies with higher EPS are seen as more profitable and, hence, better investments. However, investors should still consider other financial metrics such as P/E ratio or ROE to gain a more holistic understanding of a company’s financial position.
Investors must remember that EPS is only one part of evaluating a potential investment. Analyzing other metrics such as cash flow, debt-to-equity ratio, and revenue growth can offer additional insights into a company’s financial performance and help to ensure that an investment decision is soundly based.
Moreover, investors should strive to compare a company’s EPS with peers in the same sector to get an even better sense of its performance. By understanding a company’s relative performance and future potential, investors can make more informed decisions about their investments and, ultimately, seek higher returns.
My thorough testing awarded TradingView a stellar 4.8 stars!
With powerful stock chart analysis, pattern recognition, screening, backtesting, and a 20+ million user community, it’s a game-changer for traders.
Whether you're trading in the US or internationally, TradingView is my top pick for its unmatched features and ease of use.
Explore TradingView – Your Gateway to Smarter Trading!
Examples of Using EPS in Investing
For example, an investor might avoid companies with consistently low EPS as they may indicate inefficient operations or poor management. On the other hand, investing in companies with higher EPS could offer greater potential for returns as such firms are likely more profitable.
Similarly, investors can use EPS to identify potential takeover or merger targets. Companies with high EPS may be attractive acquisition prospects for larger firms looking to expand their operations. Furthermore, investors can also use EPS as an indicator of dividend payments – companies with higher EPS are more likely to have a greater capacity for paying out dividends to shareholders.
Finally, analyzing changes in a company’s EPS over time can provide valuable insights into its performance relative to competitors and the industry as a whole. Examining trends in EPS can help investors identify potential investment opportunities or companies that may be facing difficulties.
What Factors Influence EPS
Changes in net income, outstanding shares, dividends, and stock buybacks can influence or manipulate a company’s earnings per share (EPS) figures. Therefore, comprehending these factors is crucial.
- Net Income: The company’s net income is the most significant determinant of EPS. A higher net income generally results in a higher EPS, assuming the number of shares remains constant.
- Outstanding Shares: A company’s number of shares issued also influences its EPS. A larger number of outstanding shares can dilute EPS, while a lower number can increase it, all other things being equal.
- Dividends on Preferred Shares: If a company has issued preferred shares and pays dividends, this cost is subtracted from net income before calculating EPS.
- Capital Structure: The company’s capital structure, or the mix of debt and equity it uses to finance its operations, can affect its net income and EPS. If a company takes on a large amount of debt, interest costs will increase, which could reduce net income and EPS.
- Stock Buybacks: Companies can also impact their EPS through stock buybacks. By purchasing its own shares, a company can reduce the number of outstanding shares, increasing the EPS.
Company Growth: The growth trajectory of the company can also influence EPS. The EPS is likely to rise if a company grows and increases its earnings.
How these factors can affect the EPS
Changes in the factors mentioned above can significantly influence a company’s EPS. An increase in net income, all else being equal, will result in a higher EPS. However, if a company issues additional shares, it could dilute EPS, assuming net income remains constant. Conversely, a company can increase its EPS by buying back shares, thereby reducing the number of outstanding shares.
Dividends paid on preferred shares are subtracted from net income before calculating EPS. Hence, the more dividends a company pays on its preferred shares, the lower the EPS will be, assuming all other factors remain constant.
A company’s capital structure can also have a profound impact on EPS. If a company takes on too much debt, the increased interest costs could lower net income and EPS. In contrast, a well-balanced capital structure can optimize financial leverage and potentially enhance EPS.
Lastly, the growth trajectory of a company can influence its EPS. If a company is in a growth phase and its earnings increase, its EPS will likely increase. However, should the growth slow or earnings decline, it could result in a lower EPS.
Basic EPS
Basic EPS Definition and calculation
Basic EPS measures the net income allocated to each share of common stock outstanding. It is calculated by subtracting any dividends on preferred stock from the net income and then dividing by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period.
The formula for Basic EPS:
Basic EPS = (Net Income – Preferred Dividends) / Weighted Average Number of Common Shares Outstanding
This metric provides investors with an understanding of the company’s profitability per share.
Examples of Basic EPS
Example 1: If a company has a net income of $10 million, pays out $2 million in preferred dividends, and has a weighted average of 5 million shares outstanding, the Basic EPS would be ($10 million – $2 million) / 5 million = $1.6 per share.
Example 2: Consider a company with a net income of $500,000, no preferred dividends, and 200,000 shares outstanding. The Basic EPS would be $500,000 / 200,000 = $2.5 per share.
Example: Basic EPS Chart for Apple Inc.
In this example, I have plotted two indicators on the chart: the Basic Quarterly EPS and the Basic EPS 1 Year Growth. Notice how the one-year EPS growth highlights the acceleration in earnings.
Try TradingView’s Powerful Financial Charts
Pros of Using Basic EPS
- Easy Comparison: Basic EPS allows investors to easily compare the profitability of different companies on a per-share basis.
- Simplicity: The formula for calculating Basic EPS is straightforward to understand.
- Indication of Profitability: An increase in basic EPS over time can be a positive sign of a company’s growing profitability.
Cons of Using Basic EPS
- Overly Simplistic: Basic EPS doesn’t consider the potential dilution of shares resulting from stock options, convertible securities, or other sources.
- Manipulation: Companies could manipulate EPS through share buybacks, which reduce the number of shares outstanding and thus increase EPS.
- Not a Comprehensive Measure: While EPS can indicate profitability, it does not provide a complete picture of a company’s financial health.
How Investors Use Basic EPS
Investors can leverage Basic EPS as a valuable tool to gauge a company’s financial performance. A higher Basic EPS can signal a company’s profitability, making it an attractive investment. It allows investors to compare different companies within the same sector directly by considering the profitability on a per-share basis. Therefore, an investor could invest in a company with a higher EPS, assuming all other factors are equal.
However, investors must understand that while Basic EPS is useful, it is not infallible. It’s crucial to consider the potential dilution of shares resulting from stock options, convertible securities, or other sources, which Basic EPS does not account for. Moreover, companies could manipulate EPS through share buybacks, artificially inflating the figure.
Diluted EPS
Diluted EPS Definition and calculation
Diluted EPS is another important financial metric that offers a more comprehensive view of a company’s profitability. It considers the potential dilution of shares that could occur due to the presence of convertible securities, stock options, or other potential sources of new shares in the company. Diluted EPS is calculated by adjusting the numerator (net income) and the denominator (number of shares) of the Basic EPS formula to account for these potential new shares.
The formula for Diluted EPS:
Diluted EPS = (Net Income – Preferred Dividends + Convertible Preferred Dividends + Convertible Debt Interest*(1 – Tax Rate)) / (Weighted Average Number of Shares + Dilutive Convertible Shares + Dilutive Options + Dilutive Warrants)
This metric gives investors a more conservative estimate of the company’s profitability on a per-share basis, assuming all convertible securities are exercised.
Examples of Diluted EPS
Example 1: Consider a company with a net income of $8 million, pays out $1 million in preferred dividends, and has a weighted average of 4 million common shares outstanding. The company also has convertible preferred dividends of $500,000, convertible debt interest of $200,000 (assuming a tax rate of 30%), and potential dilutive shares from options and warrants equal to 500,000. The Diluted EPS would be calculated as ($8 million – $1 million + $500,000 + $200,000*(1-0.30)) / (4 million + 500,000) = $1.54 per share.
Example 2: A company has a net income of $2 million, no preferred dividends, and 1 million shares outstanding. The company has convertible preferred dividends of $100,000, convertible debt interest of $50,000 (assuming a tax rate of 25%), and potential dilutive shares from options and warrants equal to 200,000. The Diluted EPS would be calculated as ($2 million + $100,000 + $50,000*(1-0.25)) / (1 million + 200,000) = $1.71 per share.
Example: Diluted EPS Chart for Nvidia Corp.
In this example, I have plotted two indicators on the chart: the Diluted Quarterly EPS and the Diluted One-Year Growth. Notice the spectacular acceleration in earnings in 2023.
Try TradingView’s Powerful Financial Charts
Pros of Using Diluted EPS
- More Conservative Estimate: Diluted EPS provides a more conservative estimate of a company’s profitability by considering the potential dilution of shares.
- The breadth of Understanding: This metric gives investors a more comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial performance by considering all potential sources of new shares.
- Comparison: Like Basic EPS, Diluted EPS also allows for an easy comparison of profitability between companies on a per-share basis.
Disadvantages of Using Diluted EPS
- Complexity: The formula for calculating Diluted EPS is more complex than that of Basic EPS.
- Pessimistic View: Diluted EPS might provide a more pessimistic view of a company’s profitability as it assumes the exercise of all convertible securities.
- Potential Overemphasis: Some investors might overemphasize the importance of EPS while neglecting other important financial indicators.
How Investors Use Diluted EPS
Investors can use Diluted EPS to get a more comprehensive view of a company’s profitability. While providing a more conservative estimate, this metric assumes the conversion of all convertible securities, which may not always be true. Therefore, investors must consider both Basic and Diluted EPS while making investment decisions and not rely solely on one or the other. It’s also important to consider other financial metrics for a holistic view of a company’s financial health.
Investing In Stocks Can Be Complicated, Stock Rover Makes It Easy.
Stock Rover is our #1 rated stock investing tool for:
★ Growth Investing - With industry Leading Research Reports ★
★ Value Investing - Find Value Stocks Using Warren Buffett's Strategies ★
★ Income Investing - Harvest Safe Regular Dividends from Stocks ★

"I have been researching and investing in stocks for 20 years! I now manage all my stock investments using Stock Rover." Barry D. Moore - Founder: LiberatedStockTrader.com
Adjusted EPS
Adjusted EPS Definition and calculation
Adjusted EPS, known as Normalized EPS, is another key financial metric investors use. This measure adjusts the standard EPS to account for “one-time” events or non-operational factors that are unlikely to occur again, and that could skew an investor’s perception of a company’s normal or ‘underlying’ profitability. Such adjustments could include restructuring costs, major lawsuit expenses, or an unexpected gain or loss from the sale of assets. By excluding these unusual items, the Adjusted EPS provides a clearer picture of a company’s ongoing profitability.
The formula to calculate Adjusted EPS:
Adjusted EPS = (Net Income – One-Time Costs + One-Time Gains) / Weighted Average Number of Shares Outstanding
Note that ‘One-Time Costs’ are subtracted from Net Income, and ‘One-Time Gains’ are added. The resulting figure is then divided by the Weighted Average Number of Shares Outstanding, the same as in the Basic EPS calculation.
Examples of Adjusted EPS
Example 1: A company has a net income of $10 million, incurred $2 million in restructuring costs (a one-time cost), and has a weighted average of 5 million common shares outstanding. The Adjusted EPS would be calculated as ($10 million – $2 million) / 5 million = $1.60 per share.
Example 2: Consider a company with a net income of $3 million, gained $1 million from an unexpected asset sale (a one-time gain), and has 2 million shares outstanding. The Adjusted EPS would be calculated as ($3 million + $1 million) / 2 million = $2.00 per share.
Pros of Using Adjusted EPS
- Clarity: Adjusted EPS provides a clearer picture of a company’s ongoing profitability by excluding one-time events.
- Comparability: This metric enhances comparability between companies by removing the effects of unusual, non-recurring items.
- Investor Insight: It offers investors greater insight into a company’s sustainable financial performance.
Cons of Using Adjusted EPS
- Manipulation: Companies can manipulate Adjusted EPS by considering certain costs as “one-time” when they are not.
- Inconsistency: A lack of standardized rules for calculating Adjusted EPS leads to inconsistencies between companies.
- Overlooked Information: Some investors could overlook important information in one-time events.
How Investors Use Adjusted EPS
Investors use Adjusted EPS to evaluate a company’s ongoing profitability, separate from one-time events or non-operational items. This financial metric provides a clearer picture of a company’s sustainable earnings and is often viewed as more representative of the future earnings potential. It allows investors to make more accurate comparisons between companies by negating the effects of unusual or non-recurring items. However, investors should consider it alongside other financial indicators due to potential manipulation and lack of standardization in calculating Adjusted EPS.
Investors must also scrutinize the elements considered “one-time” costs or gains, as these can significantly impact the Adjusted EPS.
EPS Growth Rate
EPS Growth Rate is a crucial metric for investors as it provides insight into the rate at which a company’s profits increase. It is calculated by taking the difference between the current period’s EPS and the same period’s EPS in the previous year and then dividing the result by the EPS of the previous year. This figure is then multiplied by 100 to give a percentage.
EPS Growth Rate Formula:
EPS Growth Rate (%) = ((Current Period EPS – Previous Year Same Period EPS) / Previous Year Same Period EPS) * 100
An increasing EPS Growth Rate reflects a company’s ability to generate increasing profits over time, which may contribute to a rise in the company’s share price. Conversely, a decreasing EPS Growth Rate may signal a company’s declining profitability, potentially leading to a fall in share price.
Examples of EPS Growth Rate
Example 1: Suppose Company A reported an EPS of $2.00 in the current year and $1.00 in the same period of the previous year. The EPS growth rate would be calculated as (($2.00 – $1.00) / $1.00) * 100 = 100%.
Example 2: Now consider Company B, which reported an EPS of $0.50 in the current year, down from $1.00 in the same period of the previous year. The EPS growth rate would be calculated as (($0.50 – $1.00) / $1.00) * 100 = -50%.
Pros of Using EPS Growth Rate
- Performance Evaluation: The EPS Growth Rate helps gauge a company’s growing profitability, indicating high performance.
- Investment Decision: It aids investors in making informed decisions, as a high EPS Growth Rate often leads to increased confidence and investment.
- Comparison: This metric allows for a comparative analysis between companies or between different periods of a single company.
Cons of Using EPS Growth Rate
- Misleading: The EPS Growth Rate may be misleading if a company’s outstanding share number fluctuates significantly.
- Non-Recurring Items: One-time gains or losses can distort the EPS Growth Rate, presenting an inaccurate company image.
- Doesn’t Consider Capital Structure: It fails to consider the company’s capital structure, as companies with higher debt may have a higher EPS due to fewer shares despite higher risk.
Accelerating EPS
The term ‘Accelerating EPS’ is used when a company’s earnings per share (EPS) has grown exponentially over consecutive periods. Accelerating EPS is often a positive sign as it indicates a company’s increasing profitability, which may result from efficient management, increased sales, or effective cost-control measures.
Investors use this metric to identify companies that are improving their financial performance over time. A company with an accelerating EPS is likely to draw more investor interest because it suggests the company’s earnings momentum is building up, and this could potentially lead to a rising share price.
The EPS Acceleration Formula:
EPS Acceleration (%) = ((Current Period’s EPS Growth Rate – Previous Period’s EPS Growth Rate) / Previous Period’s EPS Growth Rate) * 100
Why Accelerating EPS is Important: The Evidence
William O’Neil, a renowned investor and founder of the CAN SLIM investing strategy, placed significant emphasis on accelerating Earnings Per Share (EPS) as a key indicator of a company’s potential for growth.
O’Neil’s research, highlighted in the book How to Make Money in Stocks, showed that among the 600 best-performing stocks between 1952 and 2001, three-quarters displayed earnings increases. This underscores the importance of EPS growth in determining stock performance.
O’Neil suggested that investors look for EPS to increase by 40% to 500% in bull markets. He also highlighted the significance of the last three quarters ‘ sales accelerating in percentage increases.
Examples of Accelerating EPS
Example 1: Consider Company C, whose EPS for the last three years has been $2.00, $3.00, and $4.50, respectively. The EPS growth rate for the second year was 50%, and the third year was 50%.
Example 2: Company D’s EPS for the last three years were $1.50, $1.65, and $1.90, respectively. The EPS growth rate for the second year was 10%, while for the third year, it was 15%. This shows an accelerating EPS.
Example: Accelerating EPS Chart
In this example, I have plotted two indicators on the Nvidia stock chart: the Diluted Quarterly EPS and the Diluted EPS One-Year Growth. Notice the spectacular acceleration in earnings in 2022 and 2023. In Q3 2022, Nvidia had 0.22% EPS growth, 20% in Q4, 80% in Q1 2023, and 821% in Q2. This is true EPS acceleration.
Try TradingView’s Powerful Financial Charts
Pros of Accelerating EPS
- Investment Attraction: A company with an accelerating EPS often attracts investors, indicating strong financial performance and promising future growth.
- Profitability Indication: Accelerating EPS signifies that the company is increasing its profits over time, which demonstrates efficient operations and management.
- Market Confidence: It can bolster market confidence in the company, potentially leading to a rise in its share price.
Cons of Accelerating EPS
- Short-Term View: Accelerating EPS offers a short-term view as it focuses on a particular period, thus failing to provide a comprehensive picture of a company’s overall financial health.
- Neglects Other Factors: It neglects important aspects such as a company’s cash flow, debt levels, and overall financial stability.
- Risk of Manipulation: The company might manipulate numbers to present an image of accelerating EPS.
Ever Dreamed of Beating the Stock Market
Most people think that they can't beat the market, and stock picking is a game only Wall Street insiders can win. This simply isn't true. With the right strategy, anyone can beat the market.
The LST Beat the Market Growth Stock Strategy is a proven system that has outperformed the S&P500 in 8 of the last 9 years. We provide all of the research and data needed to make informed decisions, so you no longer have to spend hours trying to find good stocks yourself.
The LST Beat the Market System Selects 35 Growth Stocks and Averages a 25.6% Annual Return
★ 35 Stocks That Already Beat The Market ★
★ Buy The Stocks & Hold For 12 Months - Then Rotate ★
★ Fully Documented Performance Track Record ★
★ Full Strategy Videos & eBook ★
Take The Pain Out Of Stock Selection With a Proven Strategy
Annual vs. Quarterly EPS
Investors often analyze a company’s earnings per share (EPS) using annual and quarterly figures. Each provides different insights and serves different purposes in investment decision-making.
Annual EPS
The annual EPS represents a company’s earnings over an entire fiscal year. It’s a key indicator of a company’s profitability and is often used to compare the performance of different companies within the same industry. The annual EPS can provide a broader perspective of a company’s long-term profitability and financial health. However, since it aggregates a full year’s earnings, the annual EPS might smooth out significant quarterly fluctuations in a company’s performance.
Quarterly EPS
On the other hand, quarterly EPS represents a company’s earnings over three months. It provides a more recent snapshot of a company’s profitability, allowing investors to track its performance and growth more regularly. A high quarterly EPS may signal a company’s positive short-term financial health. However, quarterly EPS can also be subject to seasonal variations and might not reflect a company’s annual performance trend.
EPS Analyst Estimates
Another important metric to consider when analyzing a company’s EPS is analyst estimates. Analyst estimates are forecasts of a company’s future earnings prepared by independent financial analysts. They provide additional insight into a company’s prospects and can help investors anticipate its performance in the near term.
Analysts typically release their EPS estimates at least two days before an earning announcement, allowing investors to make well-informed decisions. However, it’s important to note that analyst estimates are just predictions and are often inaccurate. As such, investors should always consider these forecasts with caution.
EPS Surprises
EPS surprises occur when a company’s reported quarterly or annual earnings per share (EPS) significantly differ from the estimates or expectations set by analysts. These surprises can have a substantial impact on a company’s stock price.
Positive EPS Surprises
A positive EPS surprise happens when the actual EPS exceeds the estimated one. This often leads to an increase in the company’s stock price, which indicates stronger financial performance than anticipated. However, it’s important to note that positive EPS surprises can also lead to inflated expectations for future performance, potentially leading to disappointment if those expectations are not met.
Negative EPS Surprises
Conversely, a negative EPS surprise occurs when the actual EPS falls short of the estimates. This typically results in a decline in the company’s stock price, suggesting weaker financial performance than investors expected. However, a negative surprise can sometimes be an opportunity for investors who believe in the company’s long-term prospects, as it may allow them to buy shares at a lower price.
Investors and analysts closely watch for EPS surprises as they can provide valuable insights into a company’s financial health and prospects. However, as with any financial metric, EPS surprises should not be used in isolation when making investment decisions. It’s also important to consider a range of other financial indicators and company fundamentals.
EPS can be a powerful tool for understanding a company’s profitability and financial health, and investors need to have an in-depth knowledge of analyst EPS estimates, EPS surprises, and EPS acceleration and growth.
FAQ
What is the best screener to find EPS growth?
Stock Rover is excellent software for conducting thorough research on company financials like EPS, PE ratio, and return on equity. It offers the broadest selection of financial metrics with charts to visualize your results effectively. Finviz and Portfolio 123 are also worth trying.
What is Earnings Per Share (EPS)?
EPS is a financial metric that calculates the portion of a company's profit allocated to each outstanding share of common stock. Investors and analysts use it to assess profitability.
How is EPS calculated?
EPS is calculated by subtracting preferred dividends from net income and dividing the result by the weighted average number of outstanding shares.
What is the best charting software for EPS?
Our testing shows TradingView is excellent for charting Basic and Diluted EPS on stock charts. TradingView's stock screener also allows you to scan for EPS growth globally across the entire stock market.
What is the significance of EPS in stock trading?
EPS is a critical indicator of a company's profitability. Higher EPS often attracts more investors, potentially driving up the stock price.
What does a negative EPS indicate?
A negative EPS indicates that a company is experiencing a net loss. This could be due to high expenses, low revenues, or both.
What's the difference between basic and diluted EPS?
Basic EPS doesn't account for convertible securities, while diluted EPS does. Diluted EPS presents a "worst-case" scenario if all convertible securities were exercised.
How can I use EPS to evaluate stocks?
EPS can help investors compare profitability among companies within the same industry. A higher EPS usually means the company is more profitable.
What is the EPS growth rate?
The EPS growth rate measures the percentage change in EPS over a specific period. It helps investors identify companies with increasing profitability.
Does a high EPS always mean a good investment?
Not necessarily. While a high EPS indicates strong profitability, investors should consider other factors like the company's debt levels, future growth prospects, and industry trends.
Can EPS be manipulated?
Yes, EPS can be manipulated through practices such as "earnings management." Investors should always analyze other financial indicators alongside EPS.
Why do some companies have a zero EPS?
A company has a zero EPS when its net income equals its preferred dividends. This means there's no income available for common stock shareholders.
What is trailing EPS?
Trailing EPS is calculated using the net income of the last four quarters. It provides a snapshot of a company's recent profitability.
What is forward EPS?
Forward EPS is an estimate of a company's EPS for future periods based on analysts' predictions.
What does 'EPS beat' mean?
An 'EPS beat' or positive earnings surprise occurs when a company's reported EPS exceeds analysts' estimates. It's often seen as a positive sign and can lead to a rise in the stock price.
How does share buyback impact EPS?
Share buybacks reduce the number of outstanding shares, which can increase the EPS if net income remains constant or grows.
Can EPS be used to calculate dividends?
Yes, the payout ratio (dividends per share divided by EPS) can help determine the portion of earnings a company pays out as dividends.
