Interest rates significantly impact the stock market. Low rates mean cheap money for businesses and consumers, boosting demand for goods and services.
This drives up companies’ profits and stock prices. Conversely, rising rates make borrowing costlier, reducing spending and causing stock prices to fall.
I will guide you through the last 60 years of economic data so you can assess the current state of the economy and, therefore, the stock market direction.
How Do Interest Rates Affect The Stock Market?
Interest rates play an important role in the stock market. When interest rates are low, businesses and consumers can access cheap money, which they use to purchase goods and services. This increased demand for goods and services causes companies’ profits to increase, driving up their stock prices. Conversely, when interest rates rise, borrowing money becomes more expensive, and people are less likely to spend their money on goods and services, which ultimately causes stock prices to drop.
The Level and Speed of Interest Rate Changes
Interest rates affect the stock market in two ways. A long-term prime interest rate below 5% encourages economic expansion, which is seen in stock market growth. A high interest rate stifles investment and causes the economy and stock market to contract. Equally important is the direction and speed of interest rate changes. Rapid interest rate increases cause stock market volatility and decline; rapid decreases can encourage quick recovery.
Firstly, we start with a brief understanding of Monetary Policy.
Video: Interest Rates vs. The Stock Market Explained
Video From The Liberated Stock Trader Pro Masterclass Course
Monetary Policy Controls Interest Rates
“Monetary policy is the process by which the government, central bank, or monetary authority of a country controls (i) the supply of money, (ii) availability of money, and (iii) cost of money or rate of interest, to attain a set of objectives oriented towards the growth and stability of the economy.” [1]
Monetary theory provides insight into how to craft optimal monetary policy.
Monetary policy is referred to as an expansionary or contractionary policy. An expansionary policy increases the total supply of money in the economy, while a contractionary policy decreases it. Expansionary policy is traditionally used to combat unemployment in a recession by lowering interest rates, while contractionary policy involves raising interest rates to combat inflation.
“Monetary policy is contrasted with Fiscal policy, which refers to government borrowing, spending, and taxation.” [2]
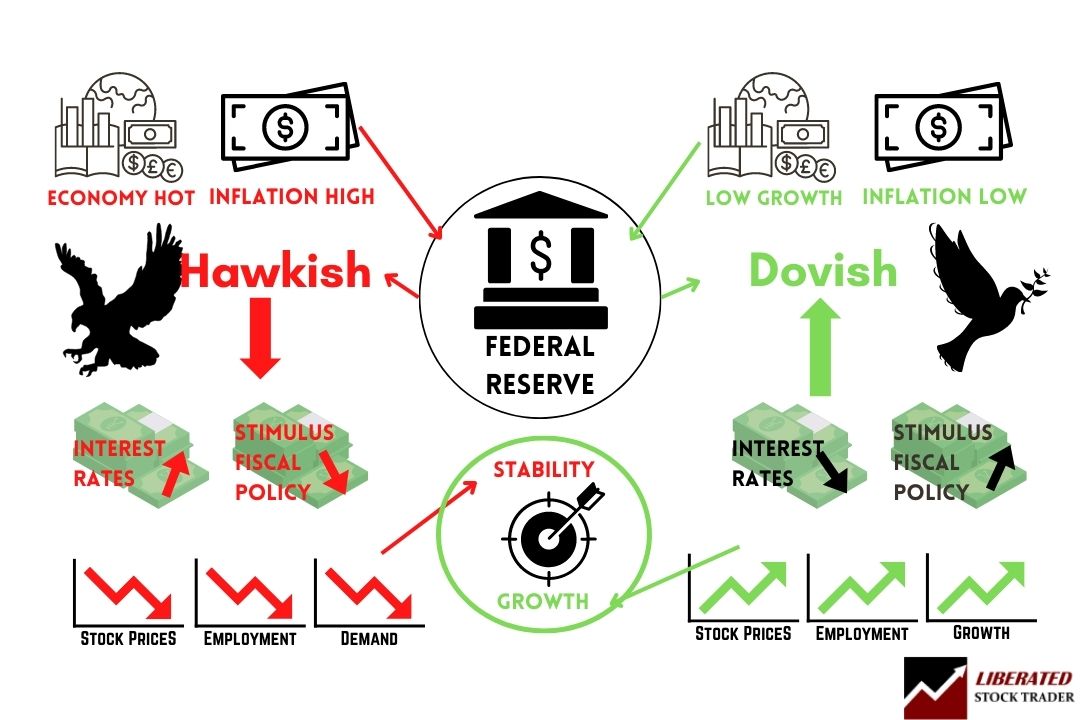
How the Federal Reserve Controls the Stock Market
The Federal Reserve is the main authority in charge of setting monetary policy. It sets the federal funds rate, which is a short-term interest rate at which banks and other financial institutions lend money to one another overnight. This rate influences other interest rates such as mortgage rates, car loan rates, credit card rates, and stock market returns.
Let’s look at what that means:
- Supply, availability, and cost of money (Prime Interest Rate) are essentially controlled by governments or government-appointed Central Banks.
- These factors are used to try to ensure economic stability.
- A government can stimulate economic growth by making money cheaper and more available. This means stimulating business and lowering unemployment, which equals stock market and real estate growth but may increase inflation.
- Increasing the cost of money via interest rates or restricting the supply of money can be used to combat the inflationary pressures in the economy, but this usually has a knock-on effect of making it more costly to borrow; therefore, companies get a lower return on the capital invested and lower profits. This drives down stock prices and real estate prices and increases unemployment.
Live Chart: Federal Funds Prime Rate.
Here is a chart of the Federal Reserve Prime Rate. Remember, rapidly increasing interest rates, especially above 5%, will cause stock market declines.
View the Fed Funds Interest Rate on Live TradingView
60 Years of Interest Rates vs. The S&P Composite Index
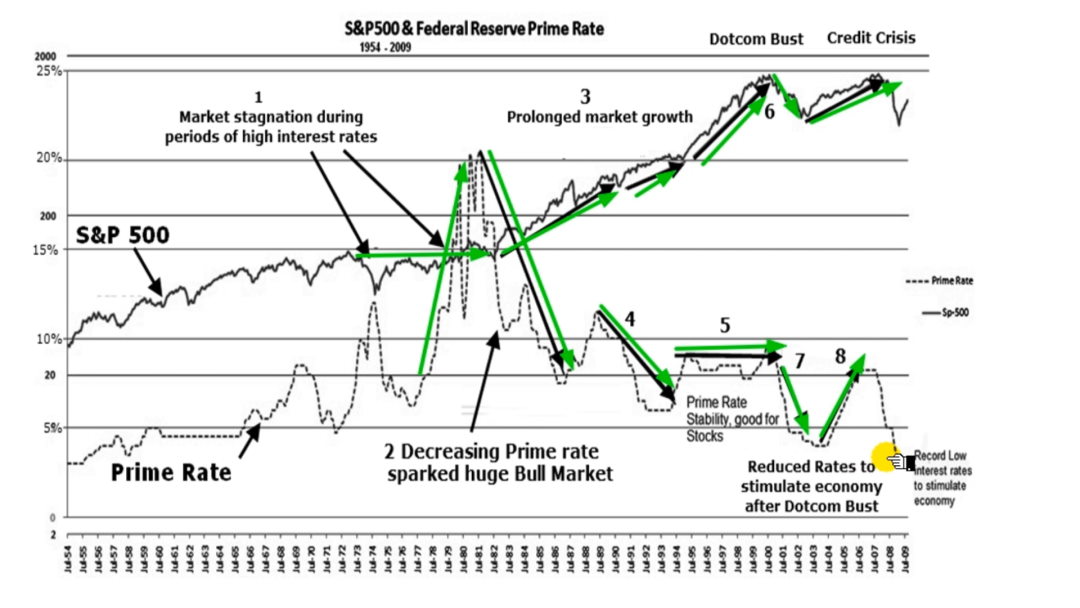
Figure 1 shows how monetary policy affects the stock market by overlaying the U.S. Prime Interest Rate on the S&P500 returns from 1954 through October 2009.
What is the prime rate? The prime rate is the cost for businesses or consumers to borrow money. The rate published is usually for favored customers with a lower risk profile; if your risk profile is higher, you may have to pay a higher interest rate.
The prime rate is important because if a company gets 80% of its capital from bank loans and has a 5% profit margin, imagine what would happen to the company’s profits if interest rates went from 5% to 15%. The company’s profit margin might be reduced by 2% or nearly halved if all things remained equal.
Therefore, a company may seek to maintain a profit margin by reducing its costs and attempting to pay back some of the debt. Reducing costs often comes in the form of reducing the workforce; therefore, unemployment increases. Companies could also increase the cost of the product or service they provide; however, this might lead to fewer sales and less profit, so they would need to shed staff anyway.
View Interest Rates on Live TradingView Charts
Example: S&P500 Index & the Federal Reserve Prime Rate
The chart here shows the effect of interest rate changes on the S&P500 Index over 60 years. As you can see, when interest rates are raised, stocks tend to lose value; however, when they are lowered, stocks typically gain in value. This is because businesses have more access to capital with lower rates and can expand their operations and increase profits. Investors also tend to seek investments with higher returns, such as stocks, when rates are down.
We can see clearly in this chart what the biggest influence over the stock market direction is.
- The mid to late ’70s saw stock market stagnation. Then, the cost of money was reduced in the form of Interest Rates. A Prime Rate above 10% has contributed strongly to a stagnant stock market at least, or at worst, a period of serious decline.
- The vigorous Prime Rate reductions in the early 1980s sparked a huge Bull Market.
- Continued low interest rates and a surge of cheap credit-fuelled an economic boom that lasted until 2000, bar the 1987 crash, which looks like only a blip compared to the overall advance.
- Rates were again reduced while the economy boomed.
- Rates increased slightly to reduce overheating but were kept under 10%. This had no significant effect on the stock market or the economy. The Prime Rate slowly increased for the five years before the 2000 Dotcom crash. Prime Rate was used to try to slow down the Developed World from overheating. It worked.
- The unrealistic expectations in the economy and the stock market were fuelled to insanity by the Internet, and the technology stocks boom had to burst. This is the idea of the bubble bursting.
- As the bubble burst, Central banks reduced interest rates to halt the further dangerous decline. Three years later, the market eventually bottomed out and resumed the usual upward trend.
- Rates slowly increased again to try to prevent overheating. This time, it did not work.
Something quite different happened in 2008 to cause one of the most violent global stock market crashes since the Depression. This time, it was not the cost of money but the money supply, the other factor mentioned in our definition of Monetary Policy. The availability of money was severely restricted because of a lack of trust between the financial institutions. None of the institutions knew how much exposure to the Sub-Prime Market existed at the time of the collapse. Therefore, the banks stopped lending to each other, drastically reducing lending to businesses and consumers. This caused a much quicker and more devastating effect on the economy than slowly increasing interest rates could have done. This was akin to somebody just turning the lights off.
You want to be a successful stock investor but don’t know where to start.
Learning stock market investing on your own can be overwhelming. There’s so much information out there, and it’s hard to know what’s true and what’s not.
Liberated Stock Trader Pro Investing Course
Our pro investing classes are the perfect way to learn stock investing. You will learn everything you need to know about financial analysis, charts, stock screening, and portfolio building so you can start building wealth today.
★ 16 Hours of Video Lessons + eBook ★
★ Complete Financial Analysis Lessons ★
★ 6 Proven Investing Strategies ★
★ Professional Grade Stock Chart Analysis Classes ★
What Is A Good Interest Rate For Stocks?
Sixty years of research shows that interest rates below 10% are good for stock market returns, below 5% produces strong stock market performance, and close to 0% produces economic crisis recovery and stock market booms. The availability of cheap money through low interest rates creates speculation in property, stocks, and commodities, which must be controlled with good financial oversight and regulation.
Will Stocks Fall When Interest Rates Rise?
My analysis shows that slow increases in interest rates over multiple years that remain below 5% will not cause stocks to fall dramatically. Any large increases in interest rates will immediately affect property prices and cause companies’ balance sheets to contract, affecting stocks.
The most common causes of stock market crashes are not interest rates but poor institutional risk management, easy access to credit, and equity bubbles.
FAQ
What is the best software for charting interest rates and inflation?
TradingView is the best software for charting interest rates, inflation, stocks, and bonds. Its connection to the Federal Reserve's QUANDL database enables powerful inflation rate charts, interest rate charts, bond market analysis, and stock charts.
What is the relationship between interest rates and the stock market?
Interest rates and the stock market have an inverse relationship. When interest rates rise, borrowing becomes more expensive, which can slow down economic growth and negatively impact stock prices. Conversely, when interest rates fall, borrowing becomes cheaper, potentially encouraging economic growth and boosting stock prices.
How do interest rates affect stock prices?
Higher interest rates can lower stock prices because they increase the cost of borrowing money, which can reduce corporate profits and dividends. Lower profits could lead to a decrease in stock prices.
What happens to the stock market when interest rates rise?
When interest rates rise, borrowing becomes more expensive for companies, which can lead to decreased profits and lower stock prices. Additionally, higher interest rates can make bonds and other fixed-income investments more attractive than stocks.
Why does the stock market go down when interest rates rise?
The stock market may decline when interest rates rise because higher borrowing costs can squeeze corporate profits, making stocks less attractive. Plus, higher interest rates often make bonds and other fixed-income investments more appealing.
Can the stock market grow in a high-interest-rate environment?
Yes, the stock market can still grow in a high-interest-rate environment. However, the rate of growth may be slower as companies may face higher borrowing costs, which could impact their profits and growth.
What happens to the stock market when interest rates fall?
When interest rates fall, borrowing becomes cheaper for companies, potentially leading to increased profits and higher stock prices. Additionally, lower interest rates can make stocks more attractive compared to bonds and other fixed-income investments.
What happens when interest rates are low for a long time?
When interest rates are low for a long period of time, it leads to asset bubbles such as the cryptocurrency, NFT, and special acquisition company (SPAC) booms. Eventually, these asset bubbles burst. Additionally, low rates for an extended period of time can lead to increased inflation and a weaker U.S. dollar, both of which can have negative impacts on the stock market.
Can a falling interest rate be bad for stocks?
Although falling interest rates can boost stock prices by making borrowing cheaper for companies, they can also signal a slowing economy. If investors believe the economy is slowing significantly, this could negatively impact stock prices.
Why do lower interest rates make stocks more attractive?
Lower interest rates make borrowing cheaper, potentially leading to increased corporate profits and higher stock dividends. This can make stocks more attractive to investors. Also, compared to bonds and other fixed-income investments, stocks offer higher returns in a low-interest-rate environment.
How do changes in the Federal Reserve's interest rates affect the stock market?
Changes in the Federal Reserve's interest rates directly impact the stock market. When the Fed raises interest rates, borrowing becomes more expensive for companies, potentially lowering stock prices. Conversely, when the Fed lowers interest rates, borrowing becomes cheaper, possibly boosting stock prices.
What role do interest rates play in stock valuation?
Interest rates are a key component in stock valuation. Higher interest rates can decrease the present value of future cash flows, potentially lowering a company's stock price. Conversely, lower interest rates can increase the value of future cash flows, boosting a company's stock price. Cash flow forecasting is a core component of value investing.
How do interest rates affect dividend stocks?
Higher interest rates can negatively impact dividend stocks. This is because as borrowing costs rise, companies may have less profit left over to distribute as dividends. Conversely, lower interest rates can potentially boost dividend payouts.
Does the stock market anticipate changes in interest rates?
Yes, the stock market anticipates changes in interest rates. Traders and investors closely watch economic indicators and statements from the Federal Reserve for clues about future interest rate moves. Investors and economists attentively monitor the Federal Reserve's stance, whether it leans towards dovishness or hawkishness.
How can investors protect their portfolios against rising interest rates?
Investors can protect their portfolios against rising interest rates by diversifying their investments, including considering bonds, real estate, and other non-stock assets. They can also consider stocks of companies that are less dependent on borrowing.
How does inflation impact the relationship between interest rates and the stock market?
Inflation can lead to higher interest rates, which can negatively impact stock prices. Conversely, deflation can lead to lower interest rates, potentially boosting stock prices. Therefore, changes in inflation can influence the relationship between interest rates and the stock market.
Are there sectors that perform well when interest rates rise?
Yes, some sectors can perform well when interest rates rise. For example, financial institutions like banks can benefit from higher interest rates because they earn more from lending.
Can interest rates affect the P/E ratio of stocks?
Yes, interest rates can affect the Price/Earnings (P/E) ratio of stocks. Higher interest rates can lower the P/E ratio because they can reduce future earnings expectations. Conversely, lower interest rates can increase the P/E ratio by boosting future earnings expectations.
How does the yield curve affect the stock market?
The yield curve, which plots the yields of bonds with different maturity dates, can affect the stock market. An inverted yield curve (where short-term interest rates are higher than long-term rates) can signal an upcoming recession, which can negatively impact stock prices.
Sources:
[1] “Monetary Policy.” Federal Reserve Board. January 3, 2006. https://www.federalreserve.gov/.
[2] B.M. Friedman “Monetary Policy,” International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences, 2001, pp. 9976-9984
You want to be a successful stock investor but don’t know where to start.
Learning stock market investing on your own can be overwhelming. There’s so much information out there, and it’s hard to know what’s true and what’s not.
Liberated Stock Trader Pro Investing Course
Our pro investing classes are the perfect way to learn stock investing. You will learn everything you need to know about financial analysis, charts, stock screening, and portfolio building so you can start building wealth today.
★ 16 Hours of Video Lessons + eBook ★
★ Complete Financial Analysis Lessons ★
★ 6 Proven Investing Strategies ★
★ Professional Grade Stock Chart Analysis Classes ★

