Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange or currency trading, is the leveraged buying and selling of currencies on the global market.
Traders can take advantage of this constantly fluctuating market by betting on which direction prices will move.
Buying and selling currency in Forex trading is for advanced speculators. Because currency fluctuations are so small, a margin is required, making it a volatile and highly risky endeavor.
Forex trading can be an exciting but daunting venture. The complex dance of buying and selling currencies, the potential for substantial profit, and the ever-present threat of risk create a thrilling arena.
But as with any financial undertaking, it’s important to tread cautiously. This comprehensive guide seeks to demystify the world of Forex trading, arming you with the knowledge to navigate the tumultuous waters of currency exchange.

What is the Forex Market?
The foreign exchange market, commonly known as Forex, is a decentralized global market where all the world’s currencies are traded. It is the world’s largest and most liquid financial market, with an average daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion.
Traders can also take advantage of leverage, allowing them to control larger positions with less capital. Leverage increases both profits and losses, so it is important to understand how to use it responsibly.
How Does Forex Trading Work?
Forex trading entails buying one currency while selling another, typically in pairs. For instance, the EUR/USD is one of the most traded forex pairs. Here, the EUR is the base currency, and the USD is the quote currency. At any given moment, the price of this pair reflects how much of the quote currency (USD) is required to purchase one unit of the base currency (EUR).
As an enabler for international trade, the foreign exchange market (FX) is the world’s biggest and most liquid market. The FX market is multiples larger than all the stock markets in the world combined. Every day, over $7 trillion of currency is exchanged.
The FX market is different because there is no central exchange. Transactions flow around the globe electronically to the exchange currently open, which means traders can trade 24 hours per day, five days per week.
My thorough testing awarded TradingView a stellar 4.8 stars!
With powerful stock chart analysis, pattern recognition, screening, backtesting, and a 20+ million user community, it’s a game-changer for traders.
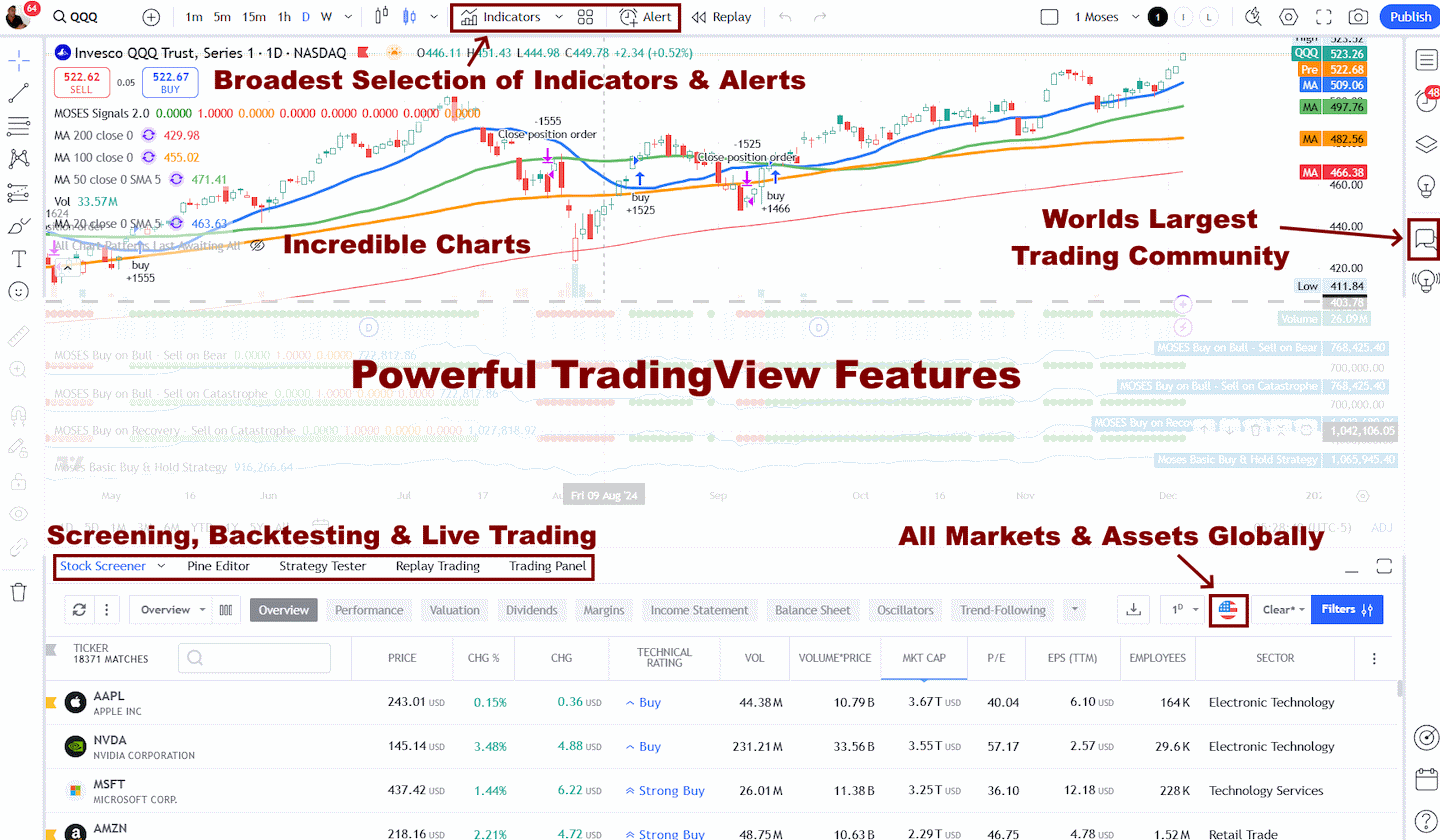
Whether you're trading in the US or internationally, TradingView is my top pick for its unmatched features and ease of use.
Explore TradingView – Your Gateway to Smarter Trading!
The Benefits
The benefits of forex trading include 24-hour trading five days a week, deep liquidity, and the availability of leverage. Leverage allows traders to control large positions with a small amount of capital, magnifying the potential for profit and loss.
The Risks
However, forex trading carries certain risks. Firstly, the use of leverage can lead to significant losses. Market volatility can also result in rapid losses if you’re on the wrong side of a trade. Learning about the market dynamics and devising an effective trading strategy requires time and effort.
Who Trades Forex?
Forex trading is carried out by individuals, institutions, and corporations speculating on the changes between two currencies. Traders use technical analysis to identify trends in price movements, which they can then use to make profitable trades.
Individuals
Individuals may use the FX market to exchange money before and after going on holiday to a foreign country. These transactions are usually committed through a bureau de change or a local bank.
Individuals can also use the FX market to profitably speculate on currencies. This involves buying and selling different currency pairs to profit from changes in exchange rates over time.
Retail FX Traders
Due to improved access and a plethora of new retail FX brokers joining the market, individuals can now speculate on the FX markets. This represents an ever-growing portion of the market. However, retail speculation is still a tiny proportion of the overall market.
Institutions
Institutions may use the FX market to speculate and profit from fluctuations in the valuations of different currency pairs. A currency pair is, for example, the USD/EUR, the value of the US Dollar versus the Euro. Major institutions such as central and commercial banks account for over half of transactions.
Central Banks
Central Banks usually hold substantial amounts of foreign exchange as an investment. The more they exchange their currency for another currency, the more they affect the value of the currencies. Depending on the economic strategy pursued, they can use this method to stabilize or strengthen a currency.
A weakening currency (meaning the currency is losing value) can be very good for businesses in that country because their exports become cheaper, boosting trade. However, this is a double-edged sword because if the country needs to import many raw materials to make their products, then the imports become more expensive.
How to Trade Forex?
To trade Forex, you need to open an account with a Forex broker. These brokers offer trading platforms where you can execute trades. Then, you need to understand the market dynamics driven by economic, political, and social factors. Learning technical analysis (interpreting price charts) and fundamental analysis (considering economic indicators) is essential.
The Best Forex Trading Platform
We recommend our partner TradingView as an excellent Forex trading platform because it offers Forex screening, heatmaps, and the world’s largest Forex trading community. TradingView has a data feed of over 100 exchanges for stocks, bonds, commodities, and Forex.
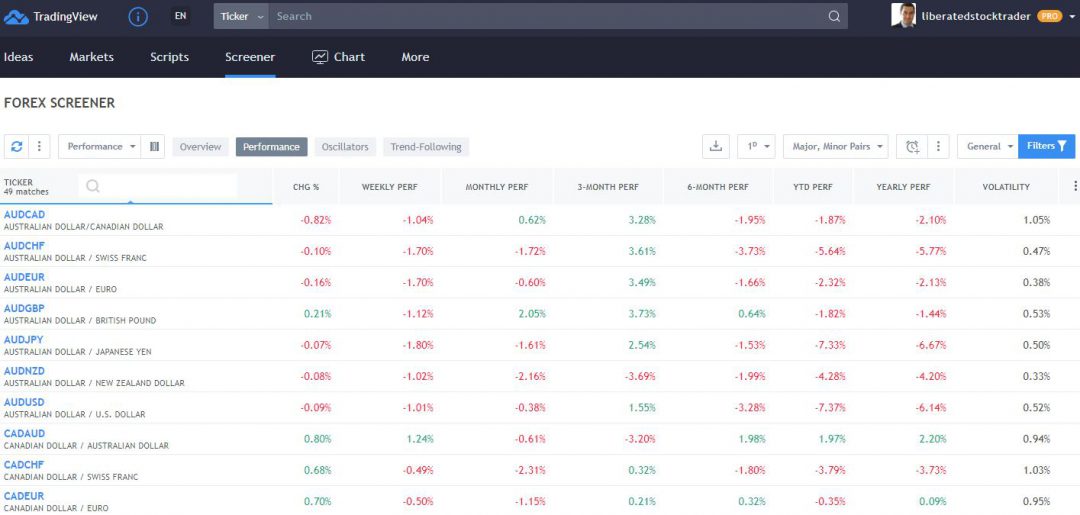
Try the Forex Screener & Trading with TradingView
Plus, you can trade on the platform directly through one of its many integrated approved brokers. So, if you’re looking for the best Forex trading platform, look no further than TradingView.
Try TradingView, Our Recommended Tool for International Traders
Global Community, Charts, Screening, Analysis & Broker Integration
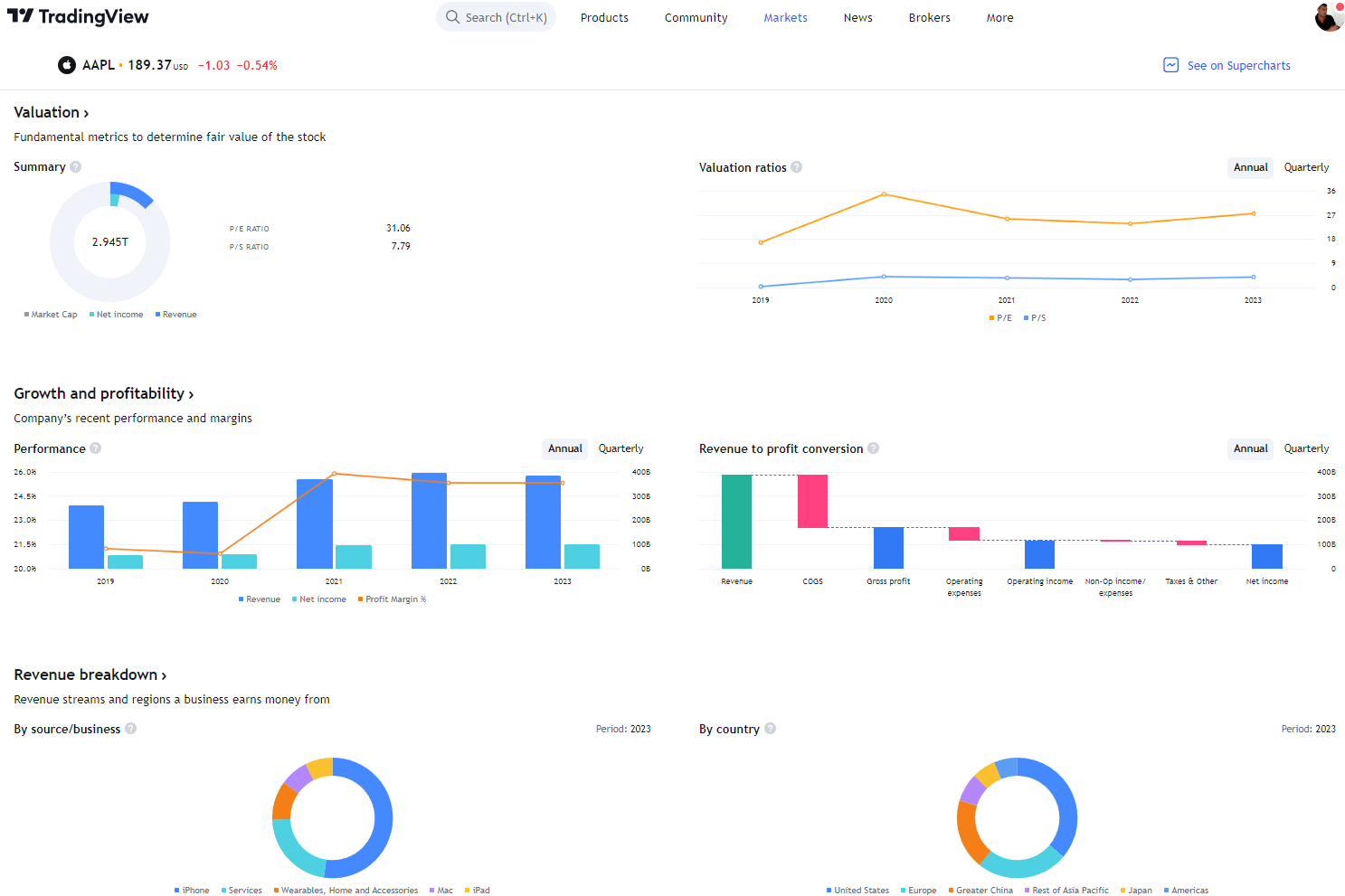
Global Financial Analysis for Free on TradingView
Forex Trading Jargon
To understand forex trading, it’s important to understand its key terms. Here are some of the most commonly used words in Forex:
- Pips – A pip is the smallest unit of price movement in a currency pair, representing either a 1/100th change or one basis point.
- Spread – The spread is the difference between the bid and ask prices in a currency pair. It’s generally quoted in pips. When you open a trade, you will be charged the spread as part of your transaction cost.
- Lot size – A lot is the standard unit size in forex trading, and it’s typically 100,000 units of the base currency in a currency pair.
- Long – Taking a long position means buying a currency pair and hoping its value will increase.
- Short – Taking a short position means selling a currency pair and hoping its value will decrease over time.
- Stop Loss – A stop loss is an order to close your position if it reaches a certain price level. This can help you limit losses in a sudden market move against your position.
- Take Profit – A take-profit order closes your position when it reaches a certain profit level. This can help you lock in profits and reduce risk.
- Leverage – Leverage increases your exposure to a financial asset without committing more money from your account. Brokers typically offer leverage in exchange for an additional fee. By increasing your leverage, you can increase the potential return on your investment and the risk of losses.
- Margin – Margin is the amount of collateral (cash or securities) a trader must deposit to open a position with their broker. The margin requirement varies depending on the type of asset being traded and the leverage the broker offers. If your position moves against you and your margin falls below the requirement, you may be issued a margin call and asked to deposit additional funds, or your position will be liquidated.
- Volatility measures how much a financial asset’s price moves relative to its average. As volatility increases, so does the risk associated with holding an asset, as there is an increased potential for large gains or losses.
- Margin Call – A margin call is an order from your broker to deposit additional funds to meet minimum balance requirements or face liquidation of some or all of your position. When trading with leverage, traders must maintain sufficient funds in their accounts.
Currency Pairs
In forex trading, currencies are traded in pairs. This means you’re simultaneously buying one currency and selling another. The two currencies in a pair are the base currency (the first one) and the quote currency (the second one). The exchange rate tells you how much of the quoted currency you need to buy one unit of the base currency.
For example, in the EUR/USD pair, EUR is the base currency, and USD is the quote currency. If the exchange rate is 1.18, you need 1.18 USD to buy one Euro.
The Carry Trade
The carry trade is a strategy used in forex trading. In this strategy, a trader borrows a currency with a low interest rate and uses it to purchase a currency with a higher interest rate. The aim is to profit from the difference in interest rates, which can be substantial, especially when leverage is applied.
For example, if the Japanese yen has an interest rate of 0.1% and the Australian dollar has an interest rate of 2.5%, a trader might borrow yen and buy Australian dollars. The trader then earns the difference between these rates of 2.4%.
However, the carry trade involves significant risks. For instance, the exchange rate between the two currencies could move in a direction that wipes out any gains from the interest rate differential. So, it’s crucial to manage risk effectively when using this strategy.
Tips for Beginners
If you’re new to forex trading, here are some tips:
- Educate Yourself: Learn as much as possible about forex trading before you start. Understand the basics of currency pairs, pips, leverage, and margin.
- Create a Trading Plan: Define your financial goals, risk tolerance, and specific strategies you will use.
- Use a Demo Account: Most forex brokers offer demo accounts where you can practice trading without risking real money.
- Start Small: When you’re ready to go live, start with a small amount of money and gradually increase your investment as you gain more experience.
- Manage Your Risks: Use risk management tools like stop loss orders to limit potential losses.
Remember, forex trading involves significant risks, including losing your entire investment. Always research and consider seeking advice from a financial advisor before starting to trade.
Understanding Currency Quotes
Currency pairs are quoted in terms of one currency per the other. For example, a currency quote of EUR/USD 1.1250 means one Euro could be exchanged for 1.1250 US Dollars. The first currency listed (Euro) is known as the base, and the second (US Dollars) is the counter currency. The rate at which one currency can be exchanged for another is known as the exchange rate.
It is important to remember that the base currency in a pair always equals 1, so if EUR/USD were quoted as 1.1250, then USD/EUR would be 0.8852 (1 / 1.1250). Knowing this, traders can easily convert between the two currencies to determine which offers a better value.
In addition to knowing how currency pairs are quoted and converted, it is also important to understand the concept of spread. Spread differs between a currency pair’s bid (sell) price and the ask (buy) price. The bid price is always lower than the asking price, and the difference between them is known as the spread.
The spread can vary over time depending on market conditions and liquidity, but it is generally a few pips for major currencies like EUR/USD. When trading currency pairs, you will need to account for the spread in your calculations to determine the true cost of a trade.
You want to be a successful stock investor but don’t know where to start.
Learning stock market investing on your own can be overwhelming. There’s so much information out there, and it’s hard to know what’s true and what’s not.
Liberated Stock Trader Pro Investing Course
Our pro investing classes are the perfect way to learn stock investing. You will learn everything you need to know about financial analysis, charts, stock screening, and portfolio building so you can start building wealth today.
★ 16 Hours of Video Lessons + eBook ★
★ Complete Financial Analysis Lessons ★
★ 6 Proven Investing Strategies ★
★ Professional Grade Stock Chart Analysis Classes ★
Trading Currency Pairs
The foreign exchange market enables the exchange of one currency into another. Therefore, they are traded in pairs. Today’s most traded pair is the USD/EUR or the EUR/USD.
Understanding Currency Pricing
Example 1. USD/EUR
In the currency pair above, the first listed currency is the USD, the base currency. The value of the base currency is always 1. The EUR, the second currency, is the counter currency. This currency’s rate will be multiplied by the base currency to calculate its exchange rate.
Example 2. GBP/JPY
In this example, the GBP is the base, and JPY is the counter currency. The value of 1 GBP is expressed in terms of JPY. So if 1 GBP = 153 JPY, a trader can buy 153 JPY with 1 GBP.
Example 3. USD/EUR 0.79
In this example, 1 US dollar can buy 0.79 of a Euro.
Example 3. EUR/USD 1.25
In this example, 1 Euro can buy 1.25 US dollars
Example 4.
- Day 1 – EUR/USD 1.25
- Day 10 – EUR/USD 1.30
In this example, on day one, the quote for EUR/Dollar means you can buy 1.25 dollars per Euro. By day ten, you could buy 1.3 dollars for each Euro. This means the base currency (Euro) has strengthened against the counter currency (Dollar).
So, if you had purchased Euros using dollars on day one and then exchanged the Euros back to dollars, you would have realized a profit of 0.05 cents per Euro owned. This would equal a gain of 4%.
A key advantage of investing in foreign exchange is that the foreign exchange markets are highly liquid and highly competitive, which means low spreads (the difference between the Bid and Ask Price).
A big disadvantage is that the price fluctuations are very small, so retail investors usually use a large amount of leverage to make a reasonable profit. Leverage is when you borrow money to add to your capital to invest; this helps to magnify the gains.
Beware of Leverage
If you have $10 to invest and borrow $90, you will have $100 to invest. With this capital, you invest and make a 10% profit. Now, your total capital is $110. When you pay the lender back $90, you are left with $20. This means you have made a 100% profit, starting at $10 and ending at $20.
The problem is that I would have lost all my money if I had made a 10% loss instead of a 10% gain on my investment. Eventually, this is what happens to most inexperienced retail investors. They lose all their money.
Trading foreign exchange is a high-risk gamble, and you are up against huge institutions and professionals worldwide.
If you intend to trade currency, you must be an expert in technical analysis and market timing.
The nature of FX is that any errors mean you lose a lot; currency trading is practiced by expert technical analysts in institutions, so do not speculate with your money unless you know what you are doing.
Forex Trading Scams
While offering significant profit potential, the world of forex trading is also rife with scams and fraudulent activity. Before getting involved in forex trading, you must research and ensure you deal with a reputable broker or company. Check online reviews and customer feedback to get an accurate picture of the provider you’re considering. Additionally, it pays to be aware of the common tactics used by scammers:
- Trading Robot Scams: Automated trading robots promise huge profits with little effort from the trader. However, these scams often use fake results to lure unsuspecting victims.
- Forex Signals Seller Scams: Some scammers sell fake trading signals that claim to accurately predict the forex market. These signals are usually worthless and lead to losses rather than profits.
- Phony Trading Investment Scams: These scams involve someone taking your money under the guise of investing it in Forex. Instead, they use your funds for personal luxury items.
One way to identify potential forex fraudsters is through their exaggerated claims of massive returns on modest investments. Forex trading itself is not a scam, but there are certainly scammers who use the industry to take advantage of unsuspecting investors.
Due to tighter regulations, forex market scams are no longer as pervasive, but some problems still exist. The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) has seen a sharp rise in forex trading scams in recent years and provides resources on identifying potential fraud.
Conduct research or consult a financial advisor when dealing with potential forex scams.
Summary
Forex trading is a legitimate industry and can be profitable, but it is important to thoroughly research potential brokers and investments before making financial decisions. The CFTC provides resources on identifying fraudulent activities, so always keep up with the latest news to protect yourself from scams.
FAQ
What is forex trading?
Forex trading, or foreign exchange or currency trading, is the buying and selling currencies on the global financial market. The goal is to profit from changes in the exchange rates between pairs of currencies.
How does forex trading work?
In forex trading, currencies are traded in pairs. You're simultaneously buying one currency and selling another. The objective is to predict which currency will appreciate or depreciate against the other.
Can I make money with forex trading?
Yes, it is possible to make money with forex trading. However, it's important to note that forex trading involves significant risk and isn't suitable for everyone. The majority of retail traders lose money when trading Forex.
How can I start forex trading?
To start forex trading, you must open a trading account with a forex broker, deposit funds into your account, and then use the broker's trading platform to buy and sell currencies. Many brokers also offer demo accounts where you can practice trading with virtual money.
What is a pip in forex trading?
A pip is a unit of measurement in forex trading representing the smallest change in value between two currencies. One pip is typically equal to a 0.0001 price change.
What is leverage in forex trading?
Leverage in forex trading is a tool that allows traders to control large amounts of money using a relatively small investment. Leverage is expressed as a ratio. For example, if your broker provides 50:1 leverage, you can trade $50 for every $1 in your account.
Is Forex trading risky?
Yes, forex trading involves high risk and isn't suitable for all investors. A high degree of leverage can work against you and for you. Before deciding to trade Forex, carefully consider your investment objectives, experience level, and risk appetite.
What is the best Forex Trading Platform?
Millions of Forex traders trust TradingView as their platform of choice. TradingView offers advanced Forex screeners, heatmaps, and live integrated trading with trusted Forex brokers worldwide. Additionally, TradingView has the largest community of Forex traders globally, all sharing ideas, strategies, and indicators.
What are the most traded currency pairs in Forex?
The most traded currency pairs in forex trading are often called the "majors," which include EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, AUD/USD, USD/CHF, NZD/USD, and USD/CAD.
What is a lot in forex trading?
A lot in forex trading is the standard unit size of a transaction. It's typically 100,000 units of the base currency. However, there are also mini (10,000), micro (1,000), and nano (100) lots available, depending on the broker.
What is a spread in forex trading?
The spread in forex trading is the difference between a currency pair's buy (ask) price and the sell (bid) price. It's essentially the broker's commission for executing the trade.
What is the best time to trade Forex?
The best time to trade Forex is when the market is most active, typically during the overlap of the London and New York trading sessions (8:00 AM to 12:00 PM EST). This is when the market has the highest volume of trades and the biggest price fluctuations.
Can I trade Forex on weekends?
The forex market is open 24 hours a day, five days a week – from Sunday evening until Friday night. So, you can't trade Forex on weekends except for some middle eastern markets, which are open on Sundays.
What is a margin call in forex trading?
A margin call is a warning from your broker that your account has fallen below the required minimum to cover your open positions. If you receive a margin call, you'll need to deposit more money into your account or close out some of your positions to return your account to the required level.
What factors affect forex prices?
Numerous factors can affect forex prices, including economic data (like GDP, employment figures, and inflation rates), political events, central bank policies, and even natural disasters. Traders use these factors to form their strategies and make trading decisions.

