A dead cat bounce is a short-term asset price recovery after a significant volatile decline, followed by a continuation of the downtrend.
☆ Research You Can Trust ☆
My analysis, research, and testing stems from 25 years of trading experience and my Financial Technician Certification with the International Federation of Technical Analysts.
Look for a short-lived rally that loses momentum quickly, often trapping bullish traders.
The somewhat macabre name implies that even a deceased feline would exhibit resilience when descending from a great height, implying that the temporary rally is more a mechanical response than a genuine recovery.
This pattern often misleads investors into thinking the downward trend has reversed, creating a trap for the unwary.

A dead cat bounce can be attributed to various factors, including short-covering, speculative trading, or even minor positive news, which does not alter the long-term fundamentals of the asset in decline. Investors and analysts closely watch these patterns to differentiate short-term recoveries from sustainable turnarounds.
Key Takeaways
- A dead cat bounce is a brief and misleading rally in a security’s price during a severe decline.
- Investors need to distinguish these from true market recoveries to avoid investment pitfalls.
- Recognizing a dead cat bounce involves understanding market dynamics and investor behavior and analyzing price movements.
Definition and Characteristics
A dead cat bounce is a short-term recovery in the price of a declining stock characterized by a short-lived rally that is typically followed by a continuation of the downtrend. This phenomenon is crucial for those active in the stock market as it can mislead investors about the true direction of price movements.
Identifying a Dead Cat Bounce
Investors look for a brief upward price recovery after a significant fall to identify a dead cat bounce. This reversal is generally short-term and often deceptive, luring investors into believing the trend has shifted positively. The challenge lies in differentiating between a true recovery and a temporary bounce.
- Indicators: Investors might use indicators such as trading volume and technical analysis patterns to recognize these events.
- Causes: Potential causes include temporary optimism, short sellers covering their positions, or market reactions to news events, which might not change the underlying fundamentals.
Technical Versus Fundamental Analysis
When examining a dead cat bounce, two main approaches are employed:
- Technical Analysis studies charts looking for patterns that indicate a temporary rally, such as decreasing volume and momentum.
- Fundamental Analysis focuses on economic indicators and market conditions. It investigates whether strong fundamentals support the price recovery or whether it is simply a reaction without a solid basis.
Both practices offer valuable insights, yet neither is foolproof in predicting the true nature of a dead cat bounce.
Our original trading research is powered by TrendSpider. As a certified market analyst, I use its state-of-the-art AI automation to recognize and test chart patterns and indicators for reliability and profitability.
✔ AI-Powered Automated Chart Analysis: Turns data into tradable insights.
✔ Point-and-Click Backtesting: Tests any indicator, pattern, or strategy in seconds.
✔ Never Miss an Opportunity: Turn backtested strategies into auto-trading bots.
Don't guess if your trading strategy works; know it with TrendSpider.
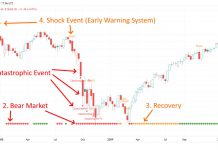
Example: How to Spot a Dead Cat Bounce
In this example, we can observe two instances of a dead cat bounce. It is interesting to note that these occurrences coincide with a price decline during the COVID-19 pandemic. Both occurrences show an increase in prices on the S&P 500 amidst a highly volatile market crash.
It is worth noting that these bounces took place during periods of relatively lower volume, suggesting that the subsequent rally would be short-lived and could be categorized as a dead cat bounce.
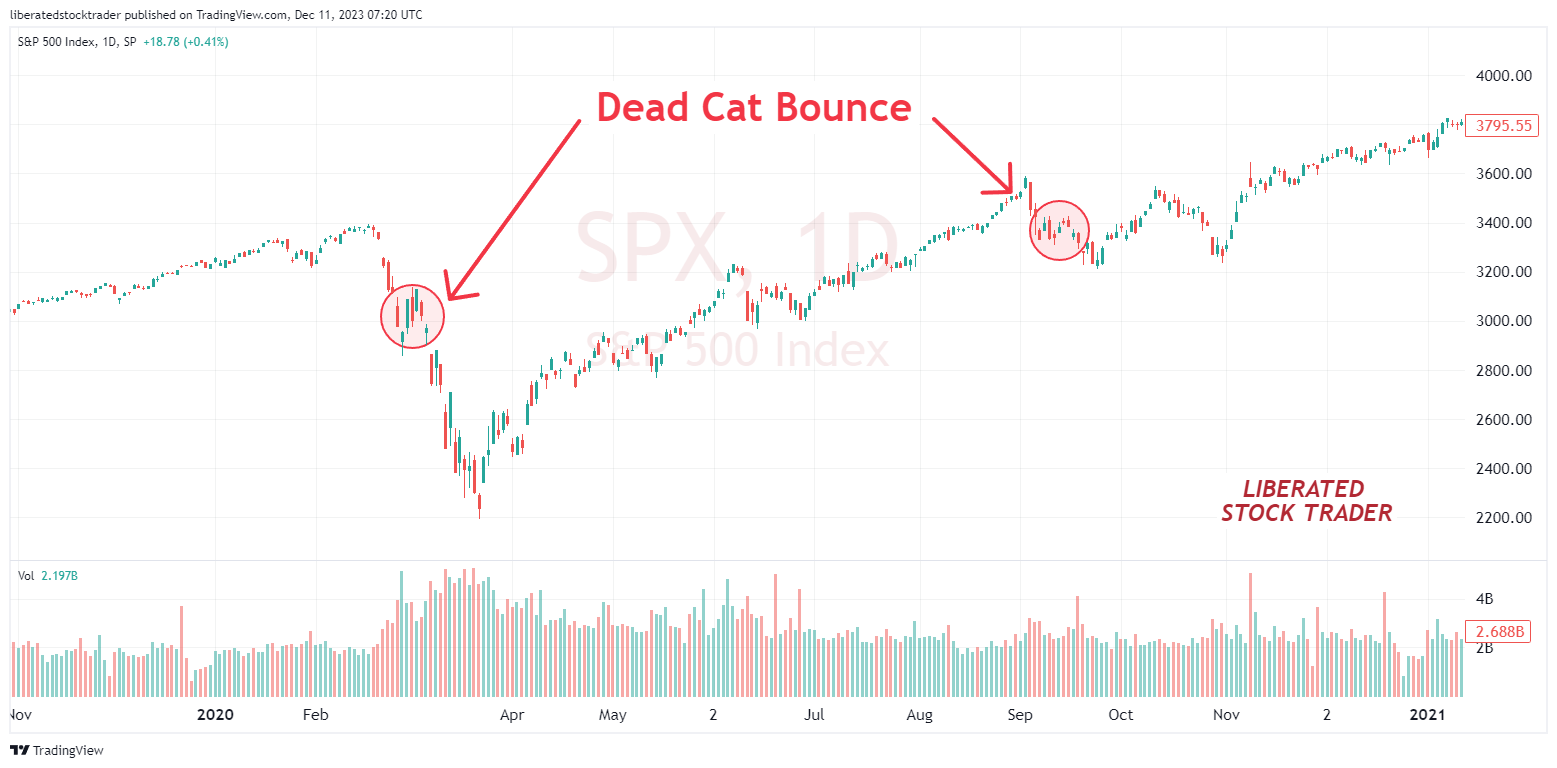
Open this Chart on TradingView
Historical Context
The term “dead cat bounce” is drawn from market events in which a stock shows a temporary recovery from a decline. Such a pattern is particularly noteworthy during economic downturns, including recessions or pandemics, when market volatility is high, and investor sentiment is fickle.
Origins of the Term
The colorful expression “dead cat bounce” suggests that even a lifeless market can show a temporary sign of life, similar to a proverbial dead cat bouncing slightly after falling from a height. The Financial Times first identified this term in print on December 7, 1985. It is now commonly applied to short-lived recoveries observed during longer-term market declines.
Notable Historical Instances
Understanding the term gains significance during real-world market turmoils. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the stock market experienced significant drops followed by quick, yet not sustained, recoveries, illustrating the concept in a modern context. The patterns observed in the stock market during this time highlighted the volatile nature of trading during unprecedented events. Historical examples have reinforced that distinguishing a dead cat bounce from a genuine market recovery is often challenging and requires careful analysis of market trends and economic indicators.
Market Dynamics and Investor Behavior
Investor behavior profoundly influences market dynamics, particularly in a bear market. The phenomenon of a Dead Cat Bounce is a testament to how investor sentiment and the actions of traders and speculators can shape stock prices and market volatility.
Role of Investor Sentiment
Investor sentiment plays a role in the occurrence of a Dead Cat Bounce. Bear market conditions often lead to a negative investor outlook, which can rapidly shift with the slightest hint of positive news. This temporary optimism can cause stocks to rally briefly before continuing their downward trend. Market volatility during this period directly reflects investors’ collective emotional responses to unfolding events.
Influence of Traders and Speculators
Traders and speculators are the liquidity engines in the stock market, often seeking to capitalize on short-term price movements. During a Dead Cat Bounce, traders may take short positions, betting that the initial recovery is unsustainable. Conversely, some speculators might see this as a buying opportunity, but such actions can lead to a quick retracement as the market reassesses the fundamentals.
Analyzing Price Movements
Recognizing patterns in stock price movements is crucial in the context of financial markets. These patterns can signal future price directions and often influence traders’ decisions.
Interpreting Stock Prices
When analyzing the stock market, understanding the behavior of stock prices is key. Securities may display a price indicating a potential market peak or a temporary resurgence during a downward trend. Interpreting these movements requires careful consideration of volume, historical price levels, and external market factors. A Dead Cat Bounce, for instance, is a temporary stock price recovery following a substantial fall, possibly misleading traders into believing a market bottom has been reached.
Volatility and Market Phases
The phases of market volatility can profoundly affect the trajectory of security prices. During these phases, the likelihood of a Dead Cat Bounce increases. Traders might observe a short-lived price increase followed by a continuation of the downtrend. It’s imperative to note that such rebounds can entice traders to take short positions, expecting the descent to resume prematurely. Identifying these phases and their characteristics is essential in distinguishing between a genuine recovery and a deceptive price pattern.
How to Avoid a Dead Cat Bounce
To avoid being lured into a dead cat bounce during a strong market decline, try using the parabolic stop and reverse (PSAR) technical indicator. A dead cat bounce is probable if the price remains below the PSAR.
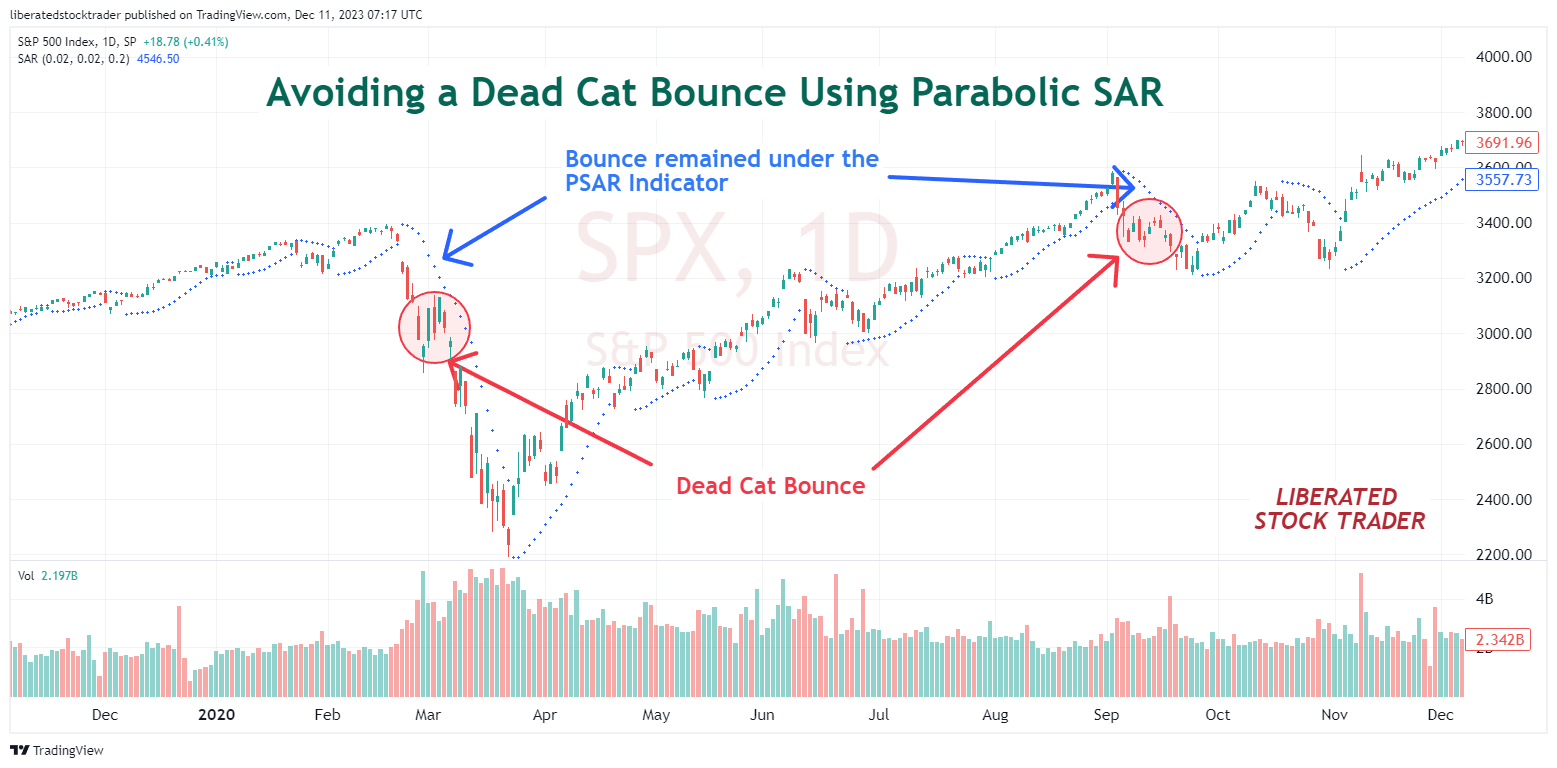
Open this Chart on TradingView
The chart example above plots the PSAR indicator over the price line. You can see that even though a dead cat bounce occurs, the price does not rise above the PSAR indicator. Using this indicator would have ensured you avoid the dead cat bounce.
Strategic Trading Decisions
In stock trading, strategic decisions involve recognizing patterns like the Dead Cat Bounce and understanding the implications on entry and exit points. These decisions are crucial, especially during a pronounced downtrend, as they can dictate the success of short-term traders and influence the stability of long-term investment portfolios.
When to Enter or Exit a Position
Entry: Traders identify an opportunity to enter a position during a Dead Cat Bounce when there’s a temporary reversal in a sustained decline. The key is to detect when the initial bouncing, signaling temporary buying pressure, is losing momentum. This can suggest the stock is still fundamentally undervalued and that the downtrend may resume.
Exit: Exiting a position—ideally at a profit—often involves short sellers capitalizing on the subsequent fall after the bounce ceases. The phrase buy low and sell high applies inversely to short sellers, who aim to sell high during the bounce and buy back lower after the expected decline.
Short-Term Trading vs Long-Term Investing
Short-Term Trading: Short-term traders thrive on volatility and look for signs of a Dead Cat Bounce for short-selling opportunities. Their investment decisions are based on quick responses to market movements and are less concerned with the long-term sustainability of a company’s stock price.
Long-Term Investing: Investors with long-term horizons may view a Dead Cat Bounce differently, potentially seeing a downtrend as a chance to add to their portfolios if they believe the stock is fundamentally sound. These investors are more willing to ride out short-term volatility, expecting a future rebound. They are less influenced by short-term market noise and are more focused on a company’s intrinsic value.
You want to be a successful stock investor but don’t know where to start.
Learning stock market investing on your own can be overwhelming. There’s so much information out there, and it’s hard to know what’s true and what’s not.
Liberated Stock Trader Pro Investing Course
Our pro investing classes are the perfect way to learn stock investing. You will learn everything you need to know about financial analysis, charts, stock screening, and portfolio building so you can start building wealth today.
★ 16 Hours of Video Lessons + eBook ★
★ Complete Financial Analysis Lessons ★
★ 6 Proven Investing Strategies ★
★ Professional Grade Stock Chart Analysis Classes ★
Challenges and Considerations
Navigating financial markets often involves differentiating between misleading signals and sustainable trends. This highlights the specific challenges and critical considerations when analyzing potential Dead Cat Bounce scenarios.
Distinguishing Temporary Rallies from True Recoveries
Investors face the challenge of distinguishing temporary rallies, such as a Dead Cat Bounce, from true recoveries. A Dead Cat Bounce represents a brief period of a rebound in the price of an asset within a longer-term bearish trend. It is characterized by a temporary increase in price, which may mistakenly be interpreted as a reversal of the preceding downtrend. The main limitation in identifying a dead cat bounce lies in its resemblance to a genuine market bottom, which is often only verified in hindsight.
True recoveries, on the other hand, signify a sustainable upward trend after a period of decline. They are often underpinned by fundamental asset value improvements or positive shifts in market sentiment.
Risks of Misinterpreting Market Signals
Misinterpreting a Dead Cat Bounce as a continuation pattern can lead to significant investor risks. Often referred to as a sucker rally, these false positives can result in premature investing decisions, where the asset’s price ultimately resumes its decline. Accurately identifying a Dead Cat Bounce requires a careful analysis of market volumes, investor sentiment, and other technical indicators to mitigate the risk of entering a position during what may only be a momentary uptick.
The Future of Dead Cat Bounces
In investment and market trends, understanding the phenomenon of dead cat bounces is essential for anticipating potential reversals or continuations of bearish markets.
Predictive Models and Market Analysis
Developing robust predictive models for detecting a dead cat bounce becomes critical. These models allow investors to differentiate between a temporary market recovery and a genuine reversal of a bullish trend. Market analysts scrutinize various indicators, such as trading volume and price patterns, to gauge whether a recovery is an actual shift in momentum or merely a temporary reprieve. Clearing of short positions often precedes these bounces, indicating that traders are attempting to capitalize on what they perceive as the bottom being reached.
Adapting to Changing Market Trends
Investors must remain agile, adapting to changing market trends to discern when a dead cat bounce signals an investment opportunity. They often look for signs that assets are oversold, which might suggest the possibility of a short-term recovery in an otherwise bearish market. On Wall Street, the savviest participants can interpret whether a recovery is a dead cat bounce before asserting that a true recession bottom has been reached. They employ historical data, real-time market analysis, and economic indicators to navigate these deceptive market patterns.
FAQ
How is a dead cat bounce identified?
A dead cat bounce is typically identified by a temporary and often surprising stock price recovery after a significant decline, followed by a continuation of the downtrend. Observers look for a short-lived rally that loses momentum quickly, often trapping bullish traders.
What does a dead cat bounce mean for investors?
For investors, a dead cat bounce can signal a false recovery, indicating that the downturn is not over. This can impact decisions on whether to sell off or hold onto assets, as there may be an anticipated further decline following the temporary rally.
Can a dead cat bounce be considered positive?
Although typically seen as a negative indicator, a dead cat bounce may be considered positive as it provides a momentary opportunity for traders to mitigate losses by selling assets before the price drops again.
How does a dead cat bounce differ from a bear market rally?
The dead cat bounce is a short-term pattern that follows a significant decline. At the same time, a bear market rally may last longer and occur during extended market lows without the immediate resumption of a downward trend, indicating a more sustained, though still temporary, recovery period.
What strategies should traders consider during a dead cat bounce period?
Traders should consider risk management strategies, possibly taking a more conservative approach by setting tight stop losses or avoiding new long positions, as the market is likely to experience further declines after the bounce.
Can a dead cat bounce occur in different markets, such as cryptocurrencies or commodities?
Yes, a dead cat bounce is not limited to equities; it can occur in various markets, including cryptocurrencies and commodities, often following a rapid decline that prompts a temporary price rise.
Investing In Stocks Can Be Complicated, Stock Rover Makes It Easy.
Stock Rover is our #1 rated stock investing tool for:
★ Growth Investing - With industry Leading Research Reports ★
★ Value Investing - Find Value Stocks Using Warren Buffett's Strategies ★
★ Income Investing - Harvest Safe Regular Dividends from Stocks ★

"I have been researching and investing in stocks for 20 years! I now manage all my stock investments using Stock Rover." Barry D. Moore - Founder: LiberatedStockTrader.com